Wednesday, December 31, 2008
Concept of Susceptibility and Vital Reactions
SUSCEPTIBILITY ACCORDING TO OXFORD DICTIONARY
-The state of being very likely to be influenced harmed or affected by anything.
e.g. susceptibility to disease or infections.
-Persons feeling which are likely to be easily hurt. i.e. susceptibility.
DEFINITION
-It is a very relative term, means wants to be magnetized by some impulse consciously or unconsciously by both mentally and physically, it is the fundamental attribute of life.
-At birth we acquire the hereditary dyspraxia and particular environmental adaptability. The combination of these two constitutes Susceptibility. It indicates the measures of defense in the body.
-Susceptibility is fundamental quality upon which all action and reaction in the physiological and pathological sense takes places in the living organism.
-Upon it depends all functioning of vital processes.
-Disease processes arising from infection or contagion are to the power of Susceptibility.
According to Dr. Hahnemann
Aphorism 30 – The human body appears to admit of being much more powerfully affected in its health by medicines (partly because we have the regulation of the dose in our own power) than by natural morbid stimuli for natural diseases are cured and overcome by suitable medicines.
Aphorism 31 – The inimical forces, partly physical, partly psychical, to which our territorial existence is exposed, which are termed morbific noxious agents, do not posses the power of morbidity deranging the health of man unconditionally but we are made ill by them only when our organism is sufficiently disposed and susceptible to the attack of the morbific cause that may be present and to be altered in its health, deranged and made to undergo abnormal sensations and function hence they do not produce disease in every one not at all times
Aphorism 32 – But it is the quite otherwise with the artificial morbific agents which term medicines. Every real medicines, namely acts at all times. Under all circumstance on every human being and produces in him its peculiar symptoms (Distinctly perceptible, if the dose be large enough so that evidently every living human organism is able to be affected and as it were inoculated with the medicinal disease at all times, and absolutely (unconditionally) which as before said is by no means the case with the natural disease.
APHORISM 33 - In accordance with this fact it is undeniably shown by all experience that the living human organism is much more disposed and has a greater liability to be acted on and to have its health derange by medicinal power than by morbific noxious agents and infectious miasms or in other words that the morbific noxious agents posses a power of morbidly deranging man’s health that is subordinate and conditional often very conditional while medical agents have an absolute unconditionanal power greatly superior to the former.
ACCORDING to Dr. Stuart Close
Susceptibility means the general quality or capability of the living organism of receiving impression, the power to react to stimuli.
ACCORDING to Dr. H.A. Robert
We may define susceptibility primarily as the reaction of organism to the external and internal influences.
According to Dr. Kent
“Susceptibility is the influence or the flow of the cause into body causes from in the direction or least resistance. If resistance appears the cause no longer flow in the influx is the flow of causes without resistance, susceptibility ceases when changes occur in the economy that bar out any more influx.
DEGREE OF SUSCEPTIBILITY
-It varies in degree in different persons and at different times in same persons.
-It diminishes both in acute and chronic diseases whose gross pathological changes have occurred
-It depends upon the nature or the disease i.e. in acute disease it stands higher.
-It also diminishes in the diseases of heart, lung, liver, kidney etc.
Susceptibility is responsible for three things
-To provides a suitable soil for the morbific agent to act and flourish with in the organism to cause disease.
-To determine the nature, seat, intensity and course of symptoms exhibited by the organism as a whole in response
-To give a highly individualized and specific response peculiar to the organism
TYPES OF SUSCEPTIBILITY
Depending upon the types or reaction exhibited by the organism, susceptibility is called as either normal or abnormal (morbid). Normal susceptibility is generally seen as a range above or below which it is said to be abnormal high as well as low susceptibility are expression of abnormal susceptibility.
The concept or susceptibility could be understood as shown in the graphs.
It is seen that different peoples reacts differently to same stimulus of touch, pains, temperature, light, food etc. these different reactions reacts the range of susceptibility in normality. It is only when there is a deviation from this range that be experience morbid susceptibility.
The change from normal to abnormal susceptibility become manifest to the physician only through sign & symptoms. Disease is responsible for modifying normal susceptibility to abnormal susceptibility where as medicine strives to modify susceptibility from to normal.
MODIFICATION OF SUSCEPTIBILITY
According to Stuart close susceptibility varies in different individuals according to age, temperament, constitution, habit, character or disease and environment.
-Susceptibility modified by age:
-Susceptibility is modified by constitution & temperament
-Susceptibility is modified by habit and environment
-Susceptibility modified by pathological conditions
-Relationship between susceptibility and immunity.
Important of susceptibility
This is generally and highly regarded as the most important guide in selection of potency. Susceptibility important in judging the amount or stimulus requires restoring health. Judgment or susceptibility is important for selection or the potency or medicines.
Modality of symptoms and susceptibility
The degree or susceptibility that is existing towards several different medicines will depends upon the degree of symptoms similar but the highest degree of susceptibility will exit towards most similar remedy similimum
The more similar and remedy the more remedy the more clearly and positively or the patient take on the peculiar and characteristics form of the remedy the greatest the susceptibly to that remedy and the higher the potency required.
BY H. A. ROBERTS (M.D.)
Everything that has life is more or less influenced by circumstances and environment
We may define susceptibility primarily as the reaction of the organism to external and internal influences
We see very frequently the susceptibility to climatic conditions, as well as all other phases of environment. One person will thrive in a rigorous climate where another will become seriously ill; one will thrive in dampness to which another would succumb. Altitude affects some individuals kindly and some adversely. The seashore improves one man's condition while it makes another man ill.
The power of assimilation and nutrition is one of the phases of susceptibility. One easily assimilates a certain kind of food while another finds the same food indigestible. “One man's meat is another man's poison
In analysing susceptibility, we find it is very largely an expression of a vacuum in the individual
In analysing susceptibility, we find it is very largely an expression of a vacuum in the individual
The vacuum attracts and pulls for .the things most needed, that are on the same plane of vibration as the want in the body.
Contagious diseases thrive in childhood because of the extremely susceptibility of the miasmatic influence; this susceptibility has an attractive force which draws to itself the disease which is on the same plane of vibration and which tends to correct this miasmatic deficiency.
Susceptibility varies in degree, in different patients, and at different times in the same patient.
Homoeopathic application of a remedy is an illustration of meeting the susceptibility and filling the vacuum that is present in the sick individual.
Susceptibility can be increased, diminished or destroyed. It therefore becomes a state of lowered resistance or attraction
Normal susceptibility and physician’s duty : It is incumbent upon us to recognize, conserve and utilize normal susceptibility, to physical environments, to foods, to remedies and to toxic agencies. It should be our aim never to use any agent or anything of any nature, or to adopt y procedure that would in the least diminish or destroy this power of susceptibility and the reaction of the organism in its normal manner. Upon this normal susceptibility and reaction depends the status of health. To do anything to diminish or destroy the normal reaction is not the province of a physician ; rather it is the province of the physician to conserve natural susceptibility, for without a recognition of this power all our efforts as physicians would be worthless. It is just as much the province of the physician to exercise conservation of susceptibility in the organism that it may act defensively against a toxin, contagion or infection, as it is to have this susceptibility react constructively to food and drink or to the curative remedy. Again, it is just as natural and important for the organism to react pathogenetically to the size and power of a dose of poison as it is for it to react to the demand for food.
On sick for physician : We must lay particular stress on demanding the con¬servation of normal susceptibility in the care of the sick, for in sickness susceptibility is exaggerated and we must be very careful to do nothing to impair it, for it is through this exaggerated reaction that we find our clue to the similar remedy In sickness it is essential to remember that it is only in the administration of the similar remedy that susceptibility is satisfied
Professor James Ewing, of Cornell University Medical College, is quoted by Dr. Stuart Close as making the following statements in 1909 in a lecture upon Immunity
Nature steps in with the Jaws of susceptibility and an influence is attracted which blooms forth as an infectious or contagious disease.
CONCLUSION
Thus we see that susceptibility and reaction are basic „ principles, and are very closely allied to the problems of s immunization. A proper concept of these principles is something that the homoeopathic physician must seriously consider; the interplay of these principles must become as second nature to him, if he wishes to use well the forces of nature in healing the sick. The similar remedy, or the SIMILAR DISEASE, SATISFIES SUSCEPTIBILITY AND ESTABLISHES IMMUNITY.
By Dr. Stuart Close
Susceptibility is one of the fundamental attributes of life. It depend all functioning, all vital processes, physiological and pathological. Digestion, assimilation, nutrition, repair, secretion, excretion, metabolism and catabolism, as well as all dis¬ease processes arising from infection or contagion depend upon the power of the organism to react to specific stimuli.
The cure and alleviation of diseases depend upon the same power of the organism to react to the impression of the curative remedy.
We shall see that the kind and degree of reaction to medicines depends upon the degree of susceptibility of the patient, and that the kind and degree of susceptibility, in any particular case or patient, depends largely .upon how the case is handled by the physician; for it is in his power to modify susceptibility. Indeed, this power to modify susceptibility is the basis of the art of the physician.
If the physician knows how to modify susceptibility in such a way as to satisfy the requirements of the sick organism and bring about a true cure, then is he a physician indeed; since cure con¬sists simply in satisfying the morbid susceptibility of the organism and putting an end to the influx of disease-producing causes.
To accomplish this he must know that susceptibility implies and includes affinity, attraction, desire, hunger, need; that these all exist and express themselves normally as states and conditions in every living being; but that they may become morbid and per¬verted and so cause disease, suffering and death.
So it is in satisfying the morbid susceptibility which constitutes disease. As hunger demands food, so disease demands medicine. But the demand is always consistent with the universal law. It is for the symptomatically similar medicine, because that is the only thing that really satisfies the susceptibility
Susceptibility as a state may be increased, diminished or destroyed.
Morbid susceptibility may be regarded as a negative or minus con-dition—a state of lowered resistance.
In health we live, act and resist without knowing it. In disease live but suffer; and know our self in conscious or uncon¬scious exaggeration.
In the case of total destruction of the susceptibility death fol¬lowed
It is a condition which reminds us of the scathing words of Jesus; "Woe unto you, Scribes and Pharisees, hypocrites! for ye are like whited sepulchers, which indeed appear beautiful outwardly, but within arc full of dead men's bones and all uncleanness.
The homoeopathic remedy, correctly chosen upon indications afforded by the anamnesis and symptoms of the disease as mani¬fested in the individual and the community, and administered in infinitesimal doses, per orain, satisfies the morbid susceptibility, supplies the need of the organism and confers a true immunity by promoting health, which is the true object to be gained.
Dr. S. P. Dey
Susceptibility is the capacity or quality of the living orga¬nism to react against any stimulus. We feel delighted when a thing joyous happens, feel morose when anything sad happens, feel chilly on cold exposure, feel uncomfortable with perspiration on exposure to heat, feel pain on being pinched ; the Vital Principle reacts against entry of any disease producing agent in our body and tries to prevent it—all these are examples of susceptibility.
By birth we possess a hereditary dyspraxia and a general adoptability
This susceptibility is modified to a great extent tinder various circumstances after birth e.g., environment, sickness, rules of hygiene, mode of living, occupation etc
In the absence of requisite susceptibility, we cannot possibly effect cure with poetized homoeopathic drugs.
Dr. Ashish Datta
The fundamental requirement of homoeopathic practice is selection of remedy accordingly to the law of similar. It is obvious that at a given point of observation out of that at a given point of observation out of a number of similar remedies only one remedy can be exactly similar to the case.
A remedy can neither be good or bad for any particular disease condition if it is homoeopathic to the case concerned it will be curative for that case i.e. proper selection of medicines with appropriate required potency.
How to assess the susceptibility
More the closer of the symptoms to the medicine indicates high the susceptible i.e. higher the potency
Selection of potency depends on:
1) Nature of the disease
2) Duration of diseases
3) Seat of disease
4) Susceptibility of the patient.
Dr. Shraddha Pathak
Every individual is born with a characteristically unique and highly specific set of innate or inherent tendency which after birth are further modified into complex patterns by environment.
The sum total or aggregate of unherited and acquired peculiarities is termed as susceptibility i.e. capacity to receive an impression.
Now a disease process (morbid alternation in general state of vital economy which expresses itself as totality of symptoms) depends on the interplay of two factors.
The offending morbific stimulus which possesses the dynamic potentiality to adverse affect our existence through any of the three planes of life namely.
Physical (Representing the outermost tangible or material aspect of our existence i.e. body.)
Mental (Comprising of Intellect, national thought, under standing and memory)
Emotional (The innermost arena of will, emotions feeling and sentiments)
The individual susceptibility or impressionability of the person exposed to the stimulus.
RELATION OF SUSCEPTIBILITY WITH FOLLOWING
1. Susceptilibty and life
Susceptibility is the fundamentals attributes of life all the physiological and pathological functions depends on this basic quality of life
” e.g. digestions, assimilations, nutrition, repair, secretion, excretion, metabolism, catabolism as well as all disease process arising from infection or contagion depends upon the power of the organism to react to specific stimuli.
2. Susceptibility and health:
An organism in perfect balance represents health.
It is always exposed to various adverse internal and external influences.
But in state of health the bodies maintain the different vital operation normally.
The Fine regulation is feasible only as long of a normal response follows a given stimulus.
This is possible only when the organism exhibits what we call normal susceptibility.
Any change or this normal susceptibility will interfere the normal response will denote a loss of balance as evidence by the abnormal sensation and functions which we call disease.
As normal susceptibility is essential for the maintenance of health, disease result from abdominal susceptibility so all reaction aim at the restoration of normal susceptibility in order to cure the disease.
3. Susceptibility and disease
Human beings one susceptible to infection and contagion in varying degree.
One man will become infected in contact with diseased individual while another person will experience no ill effects what so every one person is made ill by noxious plants. While another man can handle them with impurity.
Certain people one capable of making wonderful proving of a drug whereas other will shows no reaction what so ever. All reactions have to do with susceptibility as state may be increased or diminished.
Neither is or there is morbid state which must be considered therapeutically from the stand point the individual’s patient.
Morbid susceptibility may be regarded as negative or minus conditions a state or lowered resistance.
SUSCEPTIBILITY AND VITAL REACTIONS
A physician will have to be thoroughly conversant with the important role susceptibility plays in the following
1. Maintenance of health.
2. Evolution of the constitution.
3. Development of diathesis.
4. Development of disease.
5. Manifestations of disease.
6. Processes of recovery and cure
7. Evolution to the drug-picture.
8. Manifestation of the remedy (Remedy Reaction).
9. Determination of the dose and repetition.
SUMMERY AND CONCLUSION
We have undertaken a detailed presentation of the topic of susceptibility in relation to the various problems in the field of medical science. We have indicated that the preservation of normal susceptibility is essential to the maintenance of continued health and that any deviation from the normal range leads to the development of disease. We have shown that the restoration of normal susceptibility is the basis of cure and we have examined the therapeutic procedures in the light of this concept. We have also considered the importance of susceptibility in Pharmacology, in the evolution of the drug-pictures in homoeopathic materia medica and in determining the remedy reaction and posology. We have pointed out the dangers that are inherent in all the suppressive therapeutic procedures and have considered the scope of local applications. Finally, we have considered the problem of palliation in a patient in the grips of an incurable illness.
We could readily conclude that a sound grasp of susceptibility in general and of its correct evaluation in a particular patient is quite essential for a physician who aspires to cure in a “rapid, gentle ...... permanent..... And most harmless way”.
Saturday, December 27, 2008
50 Millesimal Scales Potency
It is a finer & latest scale of potency selection of Hahnemann which is prepared in the ratio of 1:50,000 and was mentioned clearly about its preparation, preservation and administration in 6th edition of Organon of Medicine written in the year 1842(life time of Hahnemann) and was published in the year 1921.
Nomenclature of this Scale
Dr. P.Schmidt named it as globule Method because of the fact that drug Strength of medicine prepared under this method is 50,000 times less than that contained with medicine prepared according to drop methods.
Most Important points of 50 millesimal potencies
Here are some of important points noted by all physicians.
1. Milder in action
2. Both acute as well as chronic diseases including emergency condition, even the long acting medicines & nosodes can be repeated without any fair of aggregation.
3. This scale is safe as because want of violent & dangerous aggregation.
4. Both acute & mostly chronic cases cures in quickest possible time (time of cure reduces to ½,1/4th or even shorter apho246) .
Hahnemann in his foot-note132 mentioned:
“What I said in the 5th edition of Organon, in a long note to this paragraph in order to prevent this undesirable reaction of the vital energy was all that I then had justified. But during the last four or five years, however, all these difficulties are wholly solved by my new alter but perfected method. The same carefully selected medicine may now be given daily and for months, if necessary in this way, namely, after the lower degree of potency has been used for one or two weeks in the treatment of chronic diseases, advance is made in the same way to higher degrees. ”
So it is clear if the medicine is similimum the LM potency is far better in comparison to centesimal.
Therefore it is my humble request to all for realizing the beauty & truth of LM potency for the quickest accomplishment of cure.
Preparation of Medicines
As per 6th edition of Organon in apho270-271 & foot-note150-157 we get the preparation of LM potencies.
ADMINISTRATION
HAHNEMANNIAN DIRECTION OF ADMINISTRATION AS PER $-246 0F 6th. EDITION OF ORGANON OF MEDICINE
I) the medicine selected with utmost care should be perfectly homoeopathic.
II) It should be highly potentised.
III) It should be dissolved in water.
IV) Medicine must be given in proper small dose.
V) Repetition should be made at definite intervals for quickest accomplished of
cure.
One poppy seed like globule of the similimum should be taken either in 2-ounce or 4-ounce glass phial with new water and cap and then distilled water should be poured in it up to the neck of the phial. For preservation few drops of rectified spirit should be added to this medicinal solution
and 7 or 15 or 16 doses should be marked as per necessity.
After 10-12 downward successions to the phial against a hard elastic body, one dose should be poured in a glass of distilled water (containing 7-8 spoonfuls of water, footenote134). Then after through mixing by spoon, only one teaspoonful should be taken and the rest thrown away.
Normally in acute diseases it should be repeated every 2-6 hourly, and in case of chronic diseases once or twice or weekly once twice or thrice or fortnightly. In very urgent cases may be administered every 10-15 minutes interval as per the virulence, nature, depth, and critical condition of the patient.
* After completion of first potency the next or subsequent potency should be given. For example after 0/1,0/2 should be given and thus from lower to higher i.e. ascending series of potencies should be administered .Here unlike centesimal, after administration of a single dose we do not wait for the improvement to pas off. Instead, 50-millisimal scale can be repeated along with the improvement of the patient.
When there is aggravation or return of previous symptoms we should stop the medicines. The aggravation will soon be over within a short period of time. Now same remedy is to be given in more diluted form (at long intervals) i.e. from 2nd. Or 3rd.or 4th. Glass of water according to susceptibility of the patient. In this way we can easily overcome the medicinal aggravation, which is one of the most important advantages of LM potency over centesimal potency.
DIRECTIONS FOR DISPENSING
A) Direction to the physician: -
Take one brand new phial of 120ml. With new washer and cap. Pour distilled water as much as to divide in required doses of 16/8/7/4 or less and dissolve only 0ne medicated globule of no10 of exact selected similimum in desire potency .To this solution add 5/8/10 drops of rectified spirit or good alcohol for preservation. Close the cap tightly and dispense as per direction.
B) Direction to the patient:-
Before taking the medicine each time give 10-12 downward succession against your palm and put one dose ( marked by the physician) with 3/4th. Cup of water and after thorough mixing take only one teaspoonful from it or as directed by the physician.
If there is aggravation dilute the medicine further in 2nd. Or 3rd. Or if required in 4th. Glass of water and only one teaspoonful of it will be taken & rest will be thrown away.
WITH WHAT POTENCY WE WILL START
1. as per foot note 155 of 6th. Edition of organon of Medicine” in acute fever” the small doses of lowest dynamisation degrees of these thus perfect medicinal preparations even of medicines of long continued action ( for instances, belladonna) may be repeated at short intervals.
**2. “In the treatment of chronic diseases also it is best to begin with lowest degrees of dynamisation and when necessary advance to higher, even more powerful but mildly acting degrees.”
*** 3. It is always safe to start any medicine from the lower degree i.e.from0/1 or 0/2 initially and ultimately go higher so long the improvement is going on.
WHAT IS THE NECESSITY OF SUCCESSION
Each and every dose should be succussed as clearly mentioned in footnote 133 (6th. Edition). When the best chosen homeopathic medicine- “…was dissolved in water and the first dose prove beneficial, a second or third and even smaller dose from the bottle standing undisturbed, even in intervals of few days, would prove no longer beneficial, even though the original preparation had been potentised with ten successions or I suggested later with but two successions in order to obviate this disadvantage and this according to above reasons. But thorough modification of every dose in its dynamisation degree as I herewith teach, there exist no offense, even if the doses be prepared more frequently, even if the medicine be ever so highly potentised with ever so many successions..”
MERITS OF 50-MILLESIMAL SCALE
The clinician and scientist Hahnemann found the potency up to 30th. The two succession method failed to deliver desired results. His 10 or more succession method showed too violent and dangerous medicinal aggravation. Particularly in oversensitive sick organisms Hahnemann faced many new problems. He carried on further research for 4 to 5 years to obtain desired medicinal power with rapid and long lasting penetration. On the other hand, the quantity of medicine was further reduced for avoiding further medicinal aggravation. Though difficult task indeed Hahnemann was successful in full extent and his followers, as a result, can achieve quickest accomplishment of healing art by using 50-millesimal potencies.
The centennial potencies as already stated have big gaps e.g. 6,12,30,200,1M,10M,50M,CM,DM,MM,etc.Therefore,after administration of medicines we have to wait for a long time till the aggravation is over.Moreover,as long as the improvement is on, our hands are off. But in case of 50-millesimal potency, as they ascend serially from lowest degree and there is no gap, one may say, there is no tension, no headache about the aggravation etc.One can proceed so long the improvement is on and stop the medicine at the end of the treatment when there is homeopathic aggravation. The symptom will go off from the patient and cure established. This scale of potency is considered to be the best because:-
1. In this scale, rapid action of the medicine takes place. It is gentle
because there is no medicinal aggravation. Finally, the permanent
restoration of health occurs.
2. Too frequent repetition of the medicines even those like nosodes and polychrests are possible.
3. We can avoid the medicinal aggravation by minimizing the quantity of
the medicine.
4. Qualitative power of the medicine is increased.
5. We can control the aggravation as per our need.
6. Long lasting chronic diseases can be cured within the shortest period of
time.
7. So-called incurable diseases can be cured easily by 50-millesimal
potency.
8. Acute and virulent cases can also be controlled within a short period of
time by frequent repetition.
9. In incurable cases where palliation is the only way, this potency proves
highly efficacious.
10. It works beautifully in mental diseases,
11. The medicine is much cheap and one drachm of poppy-sized globules can serve 800-1000 people.
** The above facts prove the usefulness, uniqueness and superiority of
this scale.
DEMERITS OF 50-MILLESIMAL SCALE
In this scale demerits are very limited except that there are a few
harassment to the physician, e.g.:-
i) One needs new glass phial with new cap and washer.
ii) Distilled water is needed, which should be neutral i.e. neither acidic nor
alkaline.
iii) Rectified spirit is required for preservation etc.
** the patients too find inconvenient to carry the bottles than the powder forms. Sometimes modern patients are not willing to use the repeated and frequent doses. But, from my personal experience of over 25 years, I can state that the exclusive use of 50-millesimal potencies with marvelous results. Even the unwilling patients of modern age after witnessing repeated failures of other pathies realize that this is the best mode of application of medicine.
Monday, December 15, 2008
RADAR 10 Problem
Any people who phase the problem about RADAR 10 Software installing like ""must have administrator privileges to run the program..." even if i try "run as administrator"
content me i have full solution about this problem.
EH not working still contact.
Friday, November 28, 2008
G.H.M.C. Bhopal

Introduction:
The Govt. Autonomous Homeopathic Medical College and Hospital, Bhopal was established in 1990 under the supervision of M.P. State Government, with a view to bring forth the qualified Homeopathic physicians for the purpose of serving the ailing human being in the society. The credit of starting First Degree in Homeopathy, Course B.H.M.S., Homeopathic compounder, Homeopathic Lab Technician and Naturopathy, under the Barkatullah University in this state goes to this college and the institution takes pride of the same. It is affiliated to Barkatullah University, Bhopal and recognized by Central Council of Homeopathy, New Delhi & State council of Homeopathy, Bhopal.
Right Now this institution established as a first MODAL INSTITUTION OF HOMEOPATHY.
Admission Capacity:
75 students throughout Madhya Pradesh State are admitted every year in first BHMS Course on the PHAUT Entrance Examination by VYAPAM, apart from this there is separate provision of admission for candidates outside the state & outside India (NRI). We in the process of increasing the admission capacity to above then 100 students.
College:
Situated at MACT Hill, Near Kaliyashot Dam In true natural beauty, college is equipped with best arrangements in study, well grounded by the state government. It has all modern gadgets like Laptop, Multimedia projector, Scanner, Digital camera, Printers, High speed DSL, Latest computers etc for improved method of teaching. Besides theoretical and practical knowledge of Homeopathic and allied subjects, we are also having the facility of clinical training.
Hospital:
With 50 bedded Hospital, hospital is having the facility of outdoor patient department, indoor patient dept. including Gynecology and Obstetric, Surgery (including Minor operation theater), Medicine, Pediatrics and Psychiatry subdivisions. Other than this the hospital is fully equipped with modern investigative facility like X-ray, USG, and Pathology. The institution boasts of admissions in IPD wherein students are given bedside clinical training, with demonstration of various mental conditions, traits, gaits, decubitus, behavioral & recovery of chronic cases under Classical Homoeopathic treatment.
Library:
Besides enormous book collection in the Library, it has video CD and computer CDs as teaching aid, which is provided to the students. Also has homeopathic Software.
Hostel:
Separate Boys and Girls Hostel facility is available to admitted students.
More detail visit official website of GHMC-www.ghmcbhopal.com
The Govt. Autonomous Homeopathic Medical College and Hospital, Bhopal was established in 1990 under the supervision of M.P. State Government, with a view to bring forth the qualified Homeopathic physicians for the purpose of serving the ailing human being in the society. The credit of starting First Degree in Homeopathy, Course B.H.M.S., Homeopathic compounder, Homeopathic Lab Technician and Naturopathy, under the Barkatullah University in this state goes to this college and the institution takes pride of the same. It is affiliated to Barkatullah University, Bhopal and recognized by Central Council of Homeopathy, New Delhi & State council of Homeopathy, Bhopal.
Right Now this institution established as a first MODAL INSTITUTION OF HOMEOPATHY.
Admission Capacity:
75 students throughout Madhya Pradesh State are admitted every year in first BHMS Course on the PHAUT Entrance Examination by VYAPAM, apart from this there is separate provision of admission for candidates outside the state & outside India (NRI). We in the process of increasing the admission capacity to above then 100 students.
College:
Situated at MACT Hill, Near Kaliyashot Dam In true natural beauty, college is equipped with best arrangements in study, well grounded by the state government. It has all modern gadgets like Laptop, Multimedia projector, Scanner, Digital camera, Printers, High speed DSL, Latest computers etc for improved method of teaching. Besides theoretical and practical knowledge of Homeopathic and allied subjects, we are also having the facility of clinical training.
Hospital:
With 50 bedded Hospital, hospital is having the facility of outdoor patient department, indoor patient dept. including Gynecology and Obstetric, Surgery (including Minor operation theater), Medicine, Pediatrics and Psychiatry subdivisions. Other than this the hospital is fully equipped with modern investigative facility like X-ray, USG, and Pathology. The institution boasts of admissions in IPD wherein students are given bedside clinical training, with demonstration of various mental conditions, traits, gaits, decubitus, behavioral & recovery of chronic cases under Classical Homoeopathic treatment.
Library:
Besides enormous book collection in the Library, it has video CD and computer CDs as teaching aid, which is provided to the students. Also has homeopathic Software.
Hostel:
Separate Boys and Girls Hostel facility is available to admitted students.
More detail visit official website of GHMC-www.ghmcbhopal.com
Homeopathic Software
 RADAR:
RADAR:RADAR has an impressive variety of Homoeopathic software programs for Sincere students and/or Practitioners of Homeopathy. Whether you are new to Homeopathy or are an experienced clinician, these expert system software programs can improve the quality of your Homeopathic prescribing. Further, you will be able to find the correct medicine a lot faster.
More Detail: Contact us on-http://www.radar-uk.co.uk/index.php
CARA:
CARA Pro comes with a full fledged materia medica search engine already built in. This search engine, a program named Similia, was previously available only separately. Now it has become an integral part of CARA PRO and offers many classical as well as contemporary materia medica texts. As the second player in the multi media field, after RADAR, CARA PRO supports the display of color remedy images and playing of audio and video clips. David Witko claims that full color photographs of the remedies are included, but how many and of which quality remains to be seen. There will also be spoken text on some remedies by a few of the world's leading Homeopaths.
More Detail: Contact us on-http://www.miccant.com/
Hompath Classic:
The Premium Collection has an extraordinary array of most Intelligent features- Quick, Intelligent, Accurate Symptom RecordingEven while patient is giving history, you can record symptoms, repertorize the case, filter the remedies and get the Similimum. Also crosscheck from Materia Medicae.-You can record any number of symptoms, repertorize and get similimum in just few seconds.Refer to extensive database of Themes, Cross references and Synonyms and record the symptoms from extensive source of around one million reference base.-Apply drug filtersThere are multiple permutations and combinations possible based on side affected, stage, thermal states, sex, miasm, polycrest or multiple permutations and combinations of all.-Minerals Periodic TableOpt for either Calcarea or Magnesium or from Acid group. Selection can be Horizontal group (row - series) or Vertical group (stage - column) from the periodic table.-Animal KingdomBase prescription from Insects or Mammalia or Spider or Ophidia Find correct group relationship or differentiation.-Botanical kingdom Base your drug on Compositae or Anacardiaceae or Solanaceae family or opt from flowers, seeds or roots as needed.- MiasmFilter out the remedy considering Psora, Sycosis, Tubercular or Syphilitic expressions.- SimilimumThe software can guide you with correct medicine, potency and repetition. So it is very useful for cure.-Expert system based on Masters concepts such as Kent, Boger and BoenninghausenExtremely useful, as if masters are helping you to choose the remedy to cure.-Patient Management SystemWith detailed case record under different categories, such as personal details, case history, follow-ups, plus video, audio and image can also be included. Graphical and Statistical Analysis of your various treated cases is also possible with this software. Hundreds of ready / editable patient instructions.
More Detail: Contact us on-http://www.hompath.com/
AtamA:
AtamA is a full-featured Homeopathy application geared towards the lay person and priced to be affordable. A brief description of features is provided here; see the AtamA Help file for a complete description of AtamA's capabilities or download the demo version to see for yourself.
More Detail and Download Link-http://www.abouthomeopathy.com/software/atama
Mac Repertory:
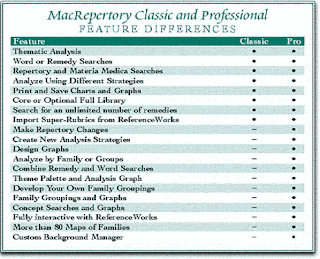
Let us introduce you to the new Mac Repertory 8. Our repertorization tool, Mac Repertory makes it easy to quickly select and analyze rubrics, get ideas for remedies, check the materia medica, do a bit of research and feel confident about your prescriptions. KHA offers two styles - Mac Repertory Pro and MacRepertory Classic. Though both are powerful tools, MacRepertory Pro offers more advanced customization and analysis features than the Classic version. Both Mac Repertory Pro and MacRepertory Classic are available with either the Core Library or the Full Library.
More Detail Click Here- http://www.kenthomeopathic.com/macrepertory.html
About Homeopathy

The Homeopathy system of medicine has developed at the end of eighteenth century by a German medical doctor, Samuel Hahnemann.
During the time of Hahnemann, many brutal ways were used to treat the patients such as leeching, cupping, blood letting and many others. These ways of treatment were so cruel that they could kill the patient as well.
Hahnemann was disgusted and disappointed with these methods of treatment that he gave up his medical profession and started devoting his time to writing and translation works. However he continued to deeply interested in medical theory & in 1790, he hit upon the homoeopathic principle that like could be cured by like. When translating, 'A treatise on the Materia medica' by the Edinburg physician, William Cullen, he read that the dry Cinchona was effective in the treatment of malaria because it was bitter & astringent & had a toning effect on the stomach. Hahnemann was not satisfied by this statement for, if it were true, then all bitter, astringent substances should likewise be effective in the treatment of malaria, & they were not.
Therefore Hahnemann decided to test the bark on himself, meeting his expectations, the symptoms on the fever occurred like could cure like. This was a part of Hippocrates teaching & sprang from the notion that symptoms could be an indication that the body was struggling to overthrow a disease, so it could be helped if the symptoms were encouraged. Thus was formulated the principle of 'Similia similibus curentur' Hahnemann named this new found therapy 'Homoeo' (similar) 'pathy' (suffering).
Subsequently, Hahnemann tested many other drugs to study the symptoms that they produced. He bravely experimented by testing the effects on himself and found many willing volunteers for the same. These experiments were known as proving and the first set of proving was conducted over about six years. As the mass of information required by these proving was assimilated, clear patterns could seen and eventually it was possible to test the substances as curative on patients with remarkable success. Although his patients were experiencing profound cures which solidly verified his theories, Hahnemann was marked as an outcast because of his method of single and minimum dosage was threatening the financial foundation of the powerful apothecaries.
But Hahnemann continued with his experiments despite the opposition and criticism from the old school of medicine. He started experimenting with a new method whereby after each dilution he would the substance rigorously. This he called 'succession' thus developing an energetic aspect of homoeopathy. It is unknown how Hahnemann reasoned this (still scientifically unexplainable) method of 'potentisation'.
In 1820, at the investigation of apothecaries, the government granted an injunction against Hahnemann dispensing his own medicines.
In 1821, Hahnemann took refuge in Cothen where he acted as a court physician to the duke of Anhalt Cothen, a former patient. From this on his many pupils and followers were also subjected to persecution as the medical orthodoxy closed ranks.
In 1835 he went to live in Paris where he had an illustrious practice with rich and poor alike receiving treatment daily in his rooms in the rue de Milan.
In 1810 Hahnemann published the 1st. of the 6 editions of 'The organism of medicine' which clearly defined his homoeopathic philosophy. In that year, after the battle of Leipzig an epidemic of ilypus had spread amongst the defeated cops of Napoleon. Hahnemann successfully treated 180 men out of which only one died. This successful treatment further spread the reputation of Homoeopathy 7 Hahnemann.
By 1821 Hahnemann had proved 60 remedies and published his materia medica in six volumes. In 1831 cholera epidemic swept the central Europe and Hahnemann successfully treated cholera patients. He also published papers on the homoeopathic treatment of the disease and instigated the first wide spread usage of Homoeopathy.
Founder of Homeopathy:
Samuel Christian Friedrich Hahnemann was born in Meissen, Saxony on 10th. April 1755, the son of porcelain painter. His early education was at home where his father taught him never to learn passively but to question everything.
By the age of 12, he was already teaching Greek to other pupils, and at 20 he had mastered eight languages and began to study medicine first at Leipzig and then at Vienna and Erlangen where he qualified in 1779.
In 1782, at the age of 27, Hahnemann married Johanna Henrietta, the daughter of an apothecary. Hahnemann became medical doctor in 1791 and quickly established a reputation as a kind and conscientious physician, who despite his own lack of wealth, often refused to accept fees for his work. Once in practice, Hahnemann became disillusioned with the medical practices of the day. Eventually he ceases to practice and pursued studies in chemistry and earned a living from his linguistic skills.
In 1790, he discovered the principle of 'likes cure likes' and then devoted himself intensively to testing out homoeopathic remedies and after 6 six years, published an article on this principle in a leading medical journal. He later published 'treatise on organon of rational medicine and materia medica'.
He accused the hostility of apothecaries and physicians and at their instigation, in 1820, Government granted an injunction against Hahnemann dispensing his own medicines.
He took refuge in Cothen and acted as the court physician to the Duke of Anhalt Cothen in 1821, where he found many pupils and followers. He published his work on chronic diseases in 1828.
His wife died in 1830 and he married for the second time to French woman, Marie Melanie d Hervily and went to live in Paris. There he had an illustrious practice with rich and poor alike receiving treatment daily in his rooms in the Rue de Milan. He died in 1843 at the age of 88.
Wednesday, October 01, 2008
Photoshop Useful Shortcut Key Chart for Windows
One of Photoshop's key features is that almost everything in it can be controlled using keyboard shortcuts. This allows the user to stay in a creative thought pattern and quickly change tools in monotonous work that requires it.
F1 - Toggles Adobe Online Help
F5 - Toggles Brush style palette
F6 - Toggles Colour, Swatches, Styles palette
F7 - Toggles Layers, Channels, Paths palette
F8 - Toggles Navigator, Info palette
F9 - Toggles Actions, History, Presets palette
Tab (Key) - Toggles all the palettes on screen
Shift + Tab (Key) - Toggles palettes on screen, excluding the Toolbar.
Main Toolbar
Key---- Action
m - Marquee Tool
l - Lasso Tool
j - Airbrush Tool
s - Rubber Stamp Tool
e - Eraser Tool
r - Blur Tool
p - Pen Tool
u - Measure Tool
k - Paint Bucket Tool
h - Hand Tool
d - Default foreground and background colors.
x - Switches between foreground and background colors
q - Switches between standard mode or quick mask mode
f - Switches between screen modes
TAB - Hides/Unhides open tools
v - Move Tool
w - Magic Wand Tool
b - Paintbrush Tool
y - History Brush Tool
n - Pencil Tool
o - Dodge Tool
t - Type Tool
g - Linear Gradient Tool
i - Eyedropper Tool
z - Zoom Tool
====================================================================
File Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + N- New
CTRL + O- Open
CTRL + ALT + O -Open As
CTRL + W- Close
CTRL + S- Save
CTRL + SHIFT + S -Save As
CTRL + ALT + S -Save a Copy
CTRL + SHIFT + P - Page Setup
CTRL + P - Print
CTRL + K- Preferences > General
====================================================================
Edit Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + Z- Undo
CTRL + X- Cut
CTRL + C- Copy
CTRL + SHIFT + C - Copy Merged
CTRL + V- Paste
CTRL + SHIFT + V- Paste Into
CTRL + T- Free Transform
CTRL + SHIFT + T- Transform > Again
====================================================================
Image Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + L- Adjust > Levels
CTRL + SHIFT + L -Adjust > Auto Levels
CTRL + ALT + SHIFT + L- Adjust > Auto Contrast
CTRL + M - Adjust > Curves
CTRL + B- Adjust > Color Balance
CTRL + U- Adjust > Hue/Saturation
CTRL + SHIFT + U- Adjust > Desaturate
CTRL + I- Adjust > Invert
CTRL + ALT + X- Extract
====================================================================
Layer Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + SHIFT + N- New > Layer
CTRL + J- New > Layer Via Copy
CTRL + SHIFT + J- New > Layer Via Cut
CTRL + G- Group with Previous
CTRL + SHIFT + G- Ungroup
CTRL + SHIFT + ]- Arrange > Bring to Front
CTRL + ] - Arrange > Bring Forward
CTRL + [- Arrange > Send Backward
CTRL + SHIFT + [ - Arrange > Send to Back
CTRL + E -Merge Down
CTRL + SHIFT + E- Merge Visible
====================================================================
Select Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + A- All
CTRL + D- Deselect
CTRL + SHIFT + D- Reselect
CTRL + SHIFT + I- Inverse
CTRL + ALT + D- Feather
============================================================================
Filter Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + F- Last Filter
CTRL + SHIFT + F- Fade
============================================================================
View Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + Y- Preview > CMYK
CTRL + SHIFT + Y- Gamut Warning
CTRL + + - Zoom In
CTRL + - - Zoom Out
CTRL + 0- Fit on Screen
CTRL + SHIFT + 0- Actual Pixels
CTRL + H - Hide Edges
CTRL + SHIFT + H- Hide Path
CTRL + R- Show Rulers
CTRL + ; - Hide Guides
CTRL + SHIFT + ; -Snap To Guides
CTRL + ALT + ; - Lock Guides
CTRL + " - Show Grid
CTRL + SHIFT + " -Snap To Grid
============================================================================
Help Menu
Key---- Action
F1- Content
====================================================================
F1 - Toggles Adobe Online Help
F5 - Toggles Brush style palette
F6 - Toggles Colour, Swatches, Styles palette
F7 - Toggles Layers, Channels, Paths palette
F8 - Toggles Navigator, Info palette
F9 - Toggles Actions, History, Presets palette
Tab (Key) - Toggles all the palettes on screen
Shift + Tab (Key) - Toggles palettes on screen, excluding the Toolbar.
Main Toolbar
Key---- Action
m - Marquee Tool
l - Lasso Tool
j - Airbrush Tool
s - Rubber Stamp Tool
e - Eraser Tool
r - Blur Tool
p - Pen Tool
u - Measure Tool
k - Paint Bucket Tool
h - Hand Tool
d - Default foreground and background colors.
x - Switches between foreground and background colors
q - Switches between standard mode or quick mask mode
f - Switches between screen modes
TAB - Hides/Unhides open tools
v - Move Tool
w - Magic Wand Tool
b - Paintbrush Tool
y - History Brush Tool
n - Pencil Tool
o - Dodge Tool
t - Type Tool
g - Linear Gradient Tool
i - Eyedropper Tool
z - Zoom Tool
====================================================================
File Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + N- New
CTRL + O- Open
CTRL + ALT + O -Open As
CTRL + W- Close
CTRL + S- Save
CTRL + SHIFT + S -Save As
CTRL + ALT + S -Save a Copy
CTRL + SHIFT + P - Page Setup
CTRL + P - Print
CTRL + K- Preferences > General
====================================================================
Edit Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + Z- Undo
CTRL + X- Cut
CTRL + C- Copy
CTRL + SHIFT + C - Copy Merged
CTRL + V- Paste
CTRL + SHIFT + V- Paste Into
CTRL + T- Free Transform
CTRL + SHIFT + T- Transform > Again
====================================================================
Image Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + L- Adjust > Levels
CTRL + SHIFT + L -Adjust > Auto Levels
CTRL + ALT + SHIFT + L- Adjust > Auto Contrast
CTRL + M - Adjust > Curves
CTRL + B- Adjust > Color Balance
CTRL + U- Adjust > Hue/Saturation
CTRL + SHIFT + U- Adjust > Desaturate
CTRL + I- Adjust > Invert
CTRL + ALT + X- Extract
====================================================================
Layer Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + SHIFT + N- New > Layer
CTRL + J- New > Layer Via Copy
CTRL + SHIFT + J- New > Layer Via Cut
CTRL + G- Group with Previous
CTRL + SHIFT + G- Ungroup
CTRL + SHIFT + ]- Arrange > Bring to Front
CTRL + ] - Arrange > Bring Forward
CTRL + [- Arrange > Send Backward
CTRL + SHIFT + [ - Arrange > Send to Back
CTRL + E -Merge Down
CTRL + SHIFT + E- Merge Visible
====================================================================
Select Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + A- All
CTRL + D- Deselect
CTRL + SHIFT + D- Reselect
CTRL + SHIFT + I- Inverse
CTRL + ALT + D- Feather
============================================================================
Filter Menu
CTRL + F- Last Filter
CTRL + SHIFT + F- Fade
============================================================================
View Menu
Key---- Action
CTRL + Y- Preview > CMYK
CTRL + SHIFT + Y- Gamut Warning
CTRL + + - Zoom In
CTRL + - - Zoom Out
CTRL + 0- Fit on Screen
CTRL + SHIFT + 0- Actual Pixels
CTRL + H - Hide Edges
CTRL + SHIFT + H- Hide Path
CTRL + R- Show Rulers
CTRL + ; - Hide Guides
CTRL + SHIFT + ; -Snap To Guides
CTRL + ALT + ; - Lock Guides
CTRL + " - Show Grid
CTRL + SHIFT + " -Snap To Grid
============================================================================
Help Menu
Key---- Action
F1- Content
====================================================================
Other Shortcuts
Key---- Action
Page Up/Down- Move view up/down 1 screen.
SHIFT + Page Up/Down- Nudge view up/down.
CTRL + Page Up/Down- Move view left/right 1 screen.
CTRL + SHIFT + - Nudge screen left/right.
Page Up/Down
CTRL + SHIFT + Z- Previous History entry.
CTRL + ALT + Z- Next History entry.
SHIFT + - - Previous blending mode.
SHIFT + + -Next blending mode.
============================================================================
Ctrl Short Cuts-
Ctrl + N - New Document Dialogue Box
Ctrl + M - Curves Dialogue Box
Ctrl + A - Selects all in the currently foreground document or currently selected layer
Ctrl + D - Deselects all in the currently foreground document or currently selected layer
Ctrl + J - Automatically creates a duplicate of the currently selected layer
Ctrl + K - Preferences Dialogue Box
Ctrl + L - Levels Dialogue Box
Ctrl + F4 - Closes current document
Ctrl + '
(Single Quote Key) - Toggles Grid Lines
Ctrl + Q - Quits Photoshop altogether
Ctrl + R - Toggles Rulers
Ctrl + U - Hue/Saturation Dialogue Box
Ctrl + O - Opens New File
Ctrl + P - Print Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Z - Undo last Action
Ctrl + Tab - Toggle between open documents
Ctrl + Shift + C - Copy Merged
Ctrl + C - Copy
Ctrl + H - Toggle Extras
Ctrl + ; - Toggle Guides
Ctrl + Shift + ; - Toggle Snap
Ctrl + X - Cut
Ctrl + Alt + Shift + X - Pattern Maker
Ctrl + V - Paste
Ctrl + Shift + V - Paste into selection
Ctrl + Alt + Shift + V - Paste Outside
Ctrl + T - Transform Tool
Ctrl + Shift + T - Repeats the last performed Transform
Shift + F5 / Shift + Backspace (Key) - Fill Layer Dialogue Box
============================================================================
Combination Number 9 Shortcuts - Ctrl + Shift / Alt-
Ctrl + Shift + O - Photoshop's File Browser
Ctrl + Shift + P - Page Setup Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Shift + S - Save As Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Shift + K - Color Setting Preferences Box
Ctrl + Shift + F - Fade Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Shift + X - Liquify Filter Tool
Ctrl + Shift + N - Create New Layer Preferences Box
Ctrl + Shift + M - Launches ImageReady
Ctrl + Shift + E - Merges all layers into a single layer
Ctrl + Alt + Z - Step Backward
Ctrl + Shift + - (Minus Sign Key) - Zoom Out
Ctrl + Shift + + (Plus Sign Key) - Zoom In
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + N - Creates a new empty layer
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + S - Save For The Web Dialogue
Ctrl + Alt (in most Dialogue Boxes) - Changes the 'Cancel' command to 'Reset'
Ctrl + Alt (in the 'Save For Web Dialogue') - Changes the 'Cancel' command to 'Reset' & the 'Done' command to
'Remember'
Ctrl + Alt + ~(Tild Symbol) - Selects the brightest area of the currently selected layer
Ctrl + Shift + I - Inverts a selection
Ctrl + Alt + X - Extract
Shift + -/+ signs(on a layer) - Toggles the different layer modes
Shift + Ctrl + Z - Step Forward
============================================================================
File Menu Shortcuts:
Ctrl+N: New Document
Ctrl+O: Open Document
Shift+Ctrl+O: Browse
Alt+Ctrl+O:Open As
Ctrl+W: Close
Ctrl+Shift+W: Close All
Ctrl+S: Save
Ctrl+Shift+S: Save As
Ctrl+Alt+S: Save a Copy
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S: Save for Web
Ctrl+Shift+P: Page Setup
Ctrl+Shift+M: Jump to Image Ready
Ctrl+Q: Exit
============================================================================
Viewing Shortcuts:
Ctrl+Y: Proof Colors
Ctrl++: Zoom In
Ctrl+-: Zoom Out
Ctrl+Alt++: Zoom In & Resize Window
Ctrl+Alt+-: Zoom Out & Resize Window
Ctrl+Alt+0: Actual Pixels
Ctrl+Shift+H: Show/Hide Target Path
Ctrl+R: Show/Hide Rulers
Ctrl+Shift+;: On/Off Snap
Ctrl+H: Show/Hide Extras
Ctrl+Alt+;: Lock Guides
Ctrl+;: Show Guides
Ctrl+': Show Grid
============================================================================
Tools Shortcuts:
A: Path Component Selection Tool
B: Paintbrush Tool
C: Crop Tool
D: Changes Default Colour Palettes To Black Foreground, White Background
E: Eraser Tool
F: Cycle Screen Modes
G: Gradient Tool
H: Hand Tool
I: Eyedropper Tool
J: Airbrush Tool
K: Slice Tool
L: Lasso Tool
M: Marquee Tool
N: Notes
O: Dodge/Burn/Sponge Tool
P: Pen Tool
Q: Quick Mask
R: Blur/Sharpen/Smudge Tool
S: Clone Stamp
T: Type Tool
U: Shape Tool
V: Move Tool
W: Magic Wand
X: Swap Colours On Colour Pallete
Y: History Brush
Z: Zoom Tool
============================================================================
Layer Shortcuts:
Ctrl+Shift+N: New Layer
Ctrl+J: Layer via Copy
Ctrl+Shift+J: Layer via Cut
Ctrl+G: Group with Previous
Ctrl+Shift+]: Bring to Front
Ctrl+]: Bring Forward
Ctrl+[: Send Backward
Ctrl+Shift+[: Send Back
Ctrl+E: Merge Layers
Ctrl+Shift+E: Merge Visible
============================================================================
Image Manipulation Shortcuts:
Ctrl+L: Adjust Levels
Ctrl+Shift+L: Adjust Auto Levels
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+L: Adjust Auto Contrast
Ctrl+M: Adjust Curves
Ctrl+B: Adjust Color Balance
Ctrl+U: Adjust Hue/Saturation
Ctrl+Shift+U: Desaturate
Ctrl+I: Invert
Ctrl+Alt+X: Extract
============================================================================
Filters Shortcuts:
Ctrl+F: Last Filter
Ctrl+Shift+F: Fade
Ctrl+Alt+X: Extract
Ctrl+Shift+X: Liquify
Ctrl+Shift+Alt+X: Pattern Make
============================================================================
Selection Shortcuts:
Ctrl+A: Select All
Ctrl+D: Deselect
Ctrl+Shift+D: Reselect
Ctrl+Shift+I: Inverse
Ctrl+Alt+D: Feather
============================================================================
Random Shortcuts:
Alt+Backspace: Fill with Forground Color
Shift+Backspace: Fill with Background Color
Alt+]: Ascend through Layers
Alt+[: Descend through Layers
Shift+Alt+]: Select Top Layer
Shift+Alt+[: Select Bottom Layer
Tab: Show/Hide All Palettes
All shortcuts may help you for better image pripration.....Enjoy
Key---- Action
Page Up/Down- Move view up/down 1 screen.
SHIFT + Page Up/Down- Nudge view up/down.
CTRL + Page Up/Down- Move view left/right 1 screen.
CTRL + SHIFT + - Nudge screen left/right.
Page Up/Down
CTRL + SHIFT + Z- Previous History entry.
CTRL + ALT + Z- Next History entry.
SHIFT + - - Previous blending mode.
SHIFT + + -Next blending mode.
============================================================================
Ctrl Short Cuts-
Ctrl + N - New Document Dialogue Box
Ctrl + M - Curves Dialogue Box
Ctrl + A - Selects all in the currently foreground document or currently selected layer
Ctrl + D - Deselects all in the currently foreground document or currently selected layer
Ctrl + J - Automatically creates a duplicate of the currently selected layer
Ctrl + K - Preferences Dialogue Box
Ctrl + L - Levels Dialogue Box
Ctrl + F4 - Closes current document
Ctrl + '
(Single Quote Key) - Toggles Grid Lines
Ctrl + Q - Quits Photoshop altogether
Ctrl + R - Toggles Rulers
Ctrl + U - Hue/Saturation Dialogue Box
Ctrl + O - Opens New File
Ctrl + P - Print Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Z - Undo last Action
Ctrl + Tab - Toggle between open documents
Ctrl + Shift + C - Copy Merged
Ctrl + C - Copy
Ctrl + H - Toggle Extras
Ctrl + ; - Toggle Guides
Ctrl + Shift + ; - Toggle Snap
Ctrl + X - Cut
Ctrl + Alt + Shift + X - Pattern Maker
Ctrl + V - Paste
Ctrl + Shift + V - Paste into selection
Ctrl + Alt + Shift + V - Paste Outside
Ctrl + T - Transform Tool
Ctrl + Shift + T - Repeats the last performed Transform
Shift + F5 / Shift + Backspace (Key) - Fill Layer Dialogue Box
============================================================================
Combination Number 9 Shortcuts - Ctrl + Shift / Alt-
Ctrl + Shift + O - Photoshop's File Browser
Ctrl + Shift + P - Page Setup Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Shift + S - Save As Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Shift + K - Color Setting Preferences Box
Ctrl + Shift + F - Fade Dialogue Box
Ctrl + Shift + X - Liquify Filter Tool
Ctrl + Shift + N - Create New Layer Preferences Box
Ctrl + Shift + M - Launches ImageReady
Ctrl + Shift + E - Merges all layers into a single layer
Ctrl + Alt + Z - Step Backward
Ctrl + Shift + - (Minus Sign Key) - Zoom Out
Ctrl + Shift + + (Plus Sign Key) - Zoom In
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + N - Creates a new empty layer
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + S - Save For The Web Dialogue
Ctrl + Alt (in most Dialogue Boxes) - Changes the 'Cancel' command to 'Reset'
Ctrl + Alt (in the 'Save For Web Dialogue') - Changes the 'Cancel' command to 'Reset' & the 'Done' command to
'Remember'
Ctrl + Alt + ~(Tild Symbol) - Selects the brightest area of the currently selected layer
Ctrl + Shift + I - Inverts a selection
Ctrl + Alt + X - Extract
Shift + -/+ signs(on a layer) - Toggles the different layer modes
Shift + Ctrl + Z - Step Forward
============================================================================
File Menu Shortcuts:
Ctrl+N: New Document
Ctrl+O: Open Document
Shift+Ctrl+O: Browse
Alt+Ctrl+O:Open As
Ctrl+W: Close
Ctrl+Shift+W: Close All
Ctrl+S: Save
Ctrl+Shift+S: Save As
Ctrl+Alt+S: Save a Copy
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S: Save for Web
Ctrl+Shift+P: Page Setup
Ctrl+Shift+M: Jump to Image Ready
Ctrl+Q: Exit
============================================================================
Viewing Shortcuts:
Ctrl+Y: Proof Colors
Ctrl++: Zoom In
Ctrl+-: Zoom Out
Ctrl+Alt++: Zoom In & Resize Window
Ctrl+Alt+-: Zoom Out & Resize Window
Ctrl+Alt+0: Actual Pixels
Ctrl+Shift+H: Show/Hide Target Path
Ctrl+R: Show/Hide Rulers
Ctrl+Shift+;: On/Off Snap
Ctrl+H: Show/Hide Extras
Ctrl+Alt+;: Lock Guides
Ctrl+;: Show Guides
Ctrl+': Show Grid
============================================================================
Tools Shortcuts:
A: Path Component Selection Tool
B: Paintbrush Tool
C: Crop Tool
D: Changes Default Colour Palettes To Black Foreground, White Background
E: Eraser Tool
F: Cycle Screen Modes
G: Gradient Tool
H: Hand Tool
I: Eyedropper Tool
J: Airbrush Tool
K: Slice Tool
L: Lasso Tool
M: Marquee Tool
N: Notes
O: Dodge/Burn/Sponge Tool
P: Pen Tool
Q: Quick Mask
R: Blur/Sharpen/Smudge Tool
S: Clone Stamp
T: Type Tool
U: Shape Tool
V: Move Tool
W: Magic Wand
X: Swap Colours On Colour Pallete
Y: History Brush
Z: Zoom Tool
============================================================================
Layer Shortcuts:
Ctrl+Shift+N: New Layer
Ctrl+J: Layer via Copy
Ctrl+Shift+J: Layer via Cut
Ctrl+G: Group with Previous
Ctrl+Shift+]: Bring to Front
Ctrl+]: Bring Forward
Ctrl+[: Send Backward
Ctrl+Shift+[: Send Back
Ctrl+E: Merge Layers
Ctrl+Shift+E: Merge Visible
============================================================================
Image Manipulation Shortcuts:
Ctrl+L: Adjust Levels
Ctrl+Shift+L: Adjust Auto Levels
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+L: Adjust Auto Contrast
Ctrl+M: Adjust Curves
Ctrl+B: Adjust Color Balance
Ctrl+U: Adjust Hue/Saturation
Ctrl+Shift+U: Desaturate
Ctrl+I: Invert
Ctrl+Alt+X: Extract
============================================================================
Filters Shortcuts:
Ctrl+F: Last Filter
Ctrl+Shift+F: Fade
Ctrl+Alt+X: Extract
Ctrl+Shift+X: Liquify
Ctrl+Shift+Alt+X: Pattern Make
============================================================================
Selection Shortcuts:
Ctrl+A: Select All
Ctrl+D: Deselect
Ctrl+Shift+D: Reselect
Ctrl+Shift+I: Inverse
Ctrl+Alt+D: Feather
============================================================================
Random Shortcuts:
Alt+Backspace: Fill with Forground Color
Shift+Backspace: Fill with Background Color
Alt+]: Ascend through Layers
Alt+[: Descend through Layers
Shift+Alt+]: Select Top Layer
Shift+Alt+[: Select Bottom Layer
Tab: Show/Hide All Palettes
All shortcuts may help you for better image pripration.....Enjoy
Tuesday, September 30, 2008
Killer Excel 2007 Shortcuts
1.Apply the outline border to the selected cells. [ Ctrl-Shift-& ]
2.Apply the Date format with the day, month, and year.[ Ctrl-Shift-# ]
3.Apply the Time format with the hour and minute, and AM or PM. [ Ctrl-Shift-@ ]
4.Enter the current time. [ Ctrl-Shift-: ]
5.Enter the current date. [ Ctrl-; ]
6.Hide the selected rows. [ Ctrl-9 ]
7.Hide the selected columns. [ Ctrl-0 ]
8.Alternate between displaying cell values and displaying formulas in the worksheet. [ Ctrl-` ]
9.Display the Find and Replace dialog box, with the Replace tab selected. [ Ctrl-H ]
10.Display the Insert Hyperlink dialog box for new hyperlink. [ Ctrl-K ]
11.Display the Print Preview window. [ Ctrl-F2 ]
12.Switch to the next workbook window. [ Ctrl-F6 ]
13.Display the Macro dialog box to create, run, edit, or delete a macro. [ Alt-F8 ]
2.Apply the Date format with the day, month, and year.[ Ctrl-Shift-# ]
3.Apply the Time format with the hour and minute, and AM or PM. [ Ctrl-Shift-@ ]
4.Enter the current time. [ Ctrl-Shift-: ]
5.Enter the current date. [ Ctrl-; ]
6.Hide the selected rows. [ Ctrl-9 ]
7.Hide the selected columns. [ Ctrl-0 ]
8.Alternate between displaying cell values and displaying formulas in the worksheet. [ Ctrl-` ]
9.Display the Find and Replace dialog box, with the Replace tab selected. [ Ctrl-H ]
10.Display the Insert Hyperlink dialog box for new hyperlink. [ Ctrl-K ]
11.Display the Print Preview window. [ Ctrl-F2 ]
12.Switch to the next workbook window. [ Ctrl-F6 ]
13.Display the Macro dialog box to create, run, edit, or delete a macro. [ Alt-F8 ]
Contact us
Dr. Surendra Singh
Fit Vital Health Care
37, Good Shepherd, Danish Kunj
Kolar Road
Bhopal, (M.P.)
Pin- 462042
Phone:
+91-755-407-6519
+91-755-407-7519
+91-997-700-2270
*Call only in official time 10:30 AM to 05:30 PM (GMT +05:30)
Mail at:
1. fitvitalservices@gmail.com
2. surendrathakur1702@gmail.com
3. surendrathakur1702@hotmail.com
Website/Blog
1. http://www.fitvital.org
2. http://www.homeopathysoftware.info
3. http://blog-fitvitalservices.blogspot.com
4. http://n-laptops.blogspot.com
Send me your detail or query:
Fit Vital Health Care
37, Good Shepherd, Danish Kunj
Kolar Road
Bhopal, (M.P.)
Pin- 462042
Phone:
+91-755-407-6519
+91-755-407-7519
+91-997-700-2270
*Call only in official time 10:30 AM to 05:30 PM (GMT +05:30)
Mail at:
1. fitvitalservices@gmail.com
2. surendrathakur1702@gmail.com
3. surendrathakur1702@hotmail.com
Website/Blog
1. http://www.fitvital.org
2. http://www.homeopathysoftware.info
3. http://blog-fitvitalservices.blogspot.com
4. http://n-laptops.blogspot.com
Send me your detail or query:
221 Microsoft Word Shortcuts
1
Ctrl + Shift + A
AllCaps
Makes the selection all capitals (toggle)
2
Alt + Ctrl + 1
ApplyHeading1
Applies Heading 1 style to the selected text
3
Alt + Ctrl + 2
ApplyHeading2
Applies Heading 2 style to the selected text
4
Alt + Ctrl + 3
ApplyHeading3
Applies Heading 3 style to the selected text
5
Ctrl + Shift + L
ApplyListBullet
Applies List Bullet style to the selected text
6
Alt + F10
AppMaximize
Enlarges the application window to full size
7
Alt + F5
AppRestore
Restores the application window to normal size
8
Ctrl+B
Bold
Makes the selection bold (toggle)
9
Ctrl + PgDn
BrowseNext
Jump to the next browse object
10
Ctrl + PgUp
BrowsePrev
Jump to the previous browse object
11
Alt + Ctrl + Home
BrowseSel
Select the next/prev browse object
12
Esc
Cancel
Terminates an action
13
Ctrl+E
CenterPara
Centers the paragraph between the indents
14
Shift+F3
ChangeCase
Changes the case of the letters in the selection
15
Left arrow
CharLeft
Moves the insertion point to the left one character
16
Shift + Left arrow
CharLeftExtend
Extends the selection to the left one character
17
Rt arrow
CharRight
Moves the insertion point to the right one character
18
Shift + Rt arrow
CharRightExtend
Extends the selection to the right one character
19
Alt + Shift + C
ClosePane
Closes the active window pane (if you are in Normal View and have, for example, the Footnote pane open)
20
Alt+Drag (or press Ctrl + Shift + F8 and drag, but Alt + Drag is far easier!)
ColumnSelect
Selects a columnar block of text
21
Ctrl +Shift+C
CopyFormat
Copies the formatting of the selection
22
Shift + F2
CopyText
Makes a copy of the selection without using the clipboard (press Return to paste)
23
Alt + F3
CreateAutoText
Adds an AutoText entry to the active template
24
Ctrl+ Backspace
DeleteBackWord
Deletes the previous word without putting it on the Clipboard
25
Ctrl + Del
DeleteWord
Deletes the next word without putting it on the Clipboard
26
Ctrl+W, Ctrl+F4
DocClose
Prompts to save the document and then closes the active window. (But doesn't intercept the menu command)
27
Ctrl + F10
DocMaximize
Enlarges the active window to full size
28
Ctrl + F7
DocMove
Changes the position of the active window
29
Ctrl + F5
DocRestore
Restores the window to normal size
30
Ctrl + F8
DocSize
Changes the size of the active window
31
Alt + Ctrl + S
DocSplit
Splits the active window horizontally and then adjusts the split
32
Alt + Shift + F9
DoFieldClick
Executes the action associated with macrobutton fields
33
Ctrl + Shift + D
DoubleUnderline
Double underlines the selection (toggle)
34
Alt R, G
DrawGroup
Groups the selected drawing objects
35
Alt R, I
DrawSnapToGrid
Sets up a grid for aligning drawing objects
36
Alt R, U
DrawUngroup
Ungroups the selected group of drawing objects
37
Ctrl+Shift+F5 (Or: Alt I, K)
EditBookmark
Brings up the bookmark dialog
38
Del
EditClear
Performs a forward delete or removes the selection without putting it on the Clipboard
39
Ctrl+C
EditCopy
Copies the selection and puts it on the Clipboard
40
Ctrl+X
EditCut
Cuts the selection and puts it on the Clipboard
41
Ctrl+F
EditFind
Finds the specified text or the specified formatting
42
F5, Ctrl+G
EditGoTo
Jumps to a specified place in the active document
43
Alt E, K
EditLinks
Allows links to be viewed, updated, opened, or removed
44
Ctrl+V
EditPaste
Inserts the Clipboard contents at the insertion point
45
Alt E, S
EditPasteSpecial
Inserts the Clipboard contents as a linked object, embedded object, or other format
46
Alt + Shift + Backspc
EditRedo
Redoes the last action that was undone
47
F4
EditRedoOrRepeat
Repeats the last command, or redoes the last action that was undone (unfortunately, doesn't work for as many commands in Word 2000 as in Word 97 and below, but this is still one of Word's most useful shortcuts, if not the most useful)
48
Ctrl+H
EditReplace
Finds the specified text or the specified formatting and replaces it
49
Ctrl+A
EditSelectAll
Selects the entire document
50
Ctrl+Z
EditUndo
Reverses the last action
51
Alt + PageDn (to select to end of column, use Alt + Shift + PgDn)
EndOfColumn
Moves to the last cell in the current table column
52
Ctrl+Shift+End
EndOfDocExtend
Extends the selection to the end of the last line of the document
53
Ctrl+End
EndOfDocument
Moves the insertion point to the end of the last line of the document
54
End
EndOfLine
Moves the insertion point to the end of the current line
55
Shift+End
EndOfLineExtend
Extends the selection to the end of the current line
56
Alt+End
EndOfRow
Moves to the last cell in the current row
57
Alt + Ctrl + PgDn
EndOfWindow
Moves the insertion point to the end of the last visible line on the screen
58
Shift + Alt + Ctrl + PgDn
EndOfWindowExtend
Extends the selection to the end of the last visible line on the screen
59
F8 (press Esc to turn off)
ExtendSelection
Turns on extend selection mode and then expands the selection with the direction keys
60
Alt + F4 (<9>)
FileCloseOrExit
Closes the current document, or if no documents are open, quits Word. Horrible command, as it makes it a long winded business to quit Word. But there's a simple solution - assign Alt+F4 to FileExit instead.
61
Alt + F4 (Word 97)
FileExit
Quits Microsoft Word and prompts to save the documents (does intercept the menu item, but not the keyboard shortcut, or the x button. An AutoExit macro is usually a better way of intercepting this).
62
NOT Ctrl+N!!
FileNew
Creates a new document or template (brings up the dialog). Note that: Word pretends that Ctrl+N is assigned to FileNew but it isn't, it's assigned to FileNewDefault You can fix this in Word 2000 by assigning Ctrl+N to the FileNewDialog command. In Word 97 the only way to fix it is to create a macro called FileNew (to do this, press Alt + F8, type "FileNew" without the quotes and Click "Create". The macro will automatically contain the code needed to make it work).
63
Ctrl+N
FileNewDefault
Creates a new document based on the Normal template.
64
Ctrl+O
FileOpen
Opens an existing document or template
65
Alt F, U
FilePageSetup
Changes the page setup of the selected sections
66
Ctrl + P
FilePrint
Prints the active document (brings up the dialog)
67
Ctrl+F2
FilePrintPreview
Displays full pages as they will be printed
68
Alt F, I
FileProperties
Shows the properties of the active document
69
Ctrl+S
FileSave
FileSave
70
Alt F, A (or F12)
FileSaveAs
Saves a copy of the document in a separate file (brings up the dialog)
71
Ctrl+Shift+F
Font
Activates the Fonts listbox on the formatting toolbar
72
Ctrl+Shift+P
FontSizeSelect
Activates the Font Size drop-down on the formatting toolbar
73
Alt + Ctrl + K
FormatAutoFormat
Automatically formats a document (or sometimes, automatically screws it up)
74
Alt O, B
FormatBordersAndShading
Changes the borders and shading of the selected paragraphs, table cells, and pictures
75
Alt O, E
FormatChangeCase
Changes the case of the letters in the selection
76
Alt O, C
FormatColumns
Changes the column format of the selected sections (brings up the dialog)
77
Alt O, D
FormatDropCap
Formats the first character of current paragraph as a dropped capital (must select it first)
78
Ctrl+D
FormatFont
Brings up the Format + Font dialog
79
Alt + Shift + R
FormatHeaderFooterLink
Links the current header/footer to the previous section (but does not intercept the button on the Header Footer toolbar)
80
Alt O, P
FormatParagraph
Brings up the Format Paragraph dialog
81
Alt O, S
FormatStyle
Applies, creates, or modifies styles
82
Alt O, T
FormatTabs
Brings up the Format Tabs dialog
83
Shift + F5
GoBack
Returns to the previous insertion point (goes back to up to 3 points, then returns to where you started; this is one of the most useful shortcuts of them all. Also useful when opening a document, if you want to g straight to where you were last editing it)
84
Ctrl + >
GrowFont
Increases the font size of the selection
85
Ctrl + ]
GrowFontOnePoint
Increases the font size of the selection by one point
86
Ctrl + T (or drag the ruler)
HangingIndent
Increases the hanging indent
87
F1
Help
Microsoft Word Help
88
Shift + F1
HelpTool
Lets you get help on a command or screen region or examine text properties
89
Ctrl + Shift + H
Hidden
Makes the selection hidden text (toggle)
90
Click on it
HyperlinkOpen
Connect to a hyperlink's address
91
Ctrl + M (or drag the ruler)
Indent
Moves the left indent to the next tab stop
92
Alt + Ctrl + M (or Alt I, M)
InsertAnnotation
Inserts a comment
93
F3
InsertAutoText
Replaces the name of the AutoText entry with its contents
94
Alt I, B
InsertBreak
Ends a page, column, or section at the insertion point
95
Alt I, C
InsertCaption
Inserts a caption above or below a selected object
96
Ctrl + Shift + Return
InsertColumnBreak
Inserts a column break at the insertion point
97
Alt + Shift + D
InsertDateField
Inserts a date field
98
Alt + Ctrl + D
InsertEndnoteNow
Inserts an endnote reference at the insertion point without displaying the dialog
99
Alt I, F
InsertField
Inserts a field in the active document
100
Ctrl+F9
InsertFieldChars
Inserts an empty field with the enclosing field characters
101
Alt I, L
InsertFile
Inserts the text of another file into the active document
102
Alt I, N
InsertFootnote
Inserts a footnote or endnote reference at the insertion point
103
Alt + Ctrl + F
InsertFootnoteNow
Inserts a footnote reference at the insertion point without displaying the dialog
104
Ctrl + K
InsertHyperlink
Insert Hyperlink
105
Alt I, D
InsertIndexAndTables
Inserts an index or a table of contents, figures, or authorities into the document
106
Alt + Ctrl + L
InsertListNumField
Inserts a ListNum Field
107
Alt + Shift + F
InsertMergeField
Brings up a dialog to insert a mail merge field at the insertion point. (It does not intercept the button on the Mail merge. toolbar)
108
Ctrl + Return
InsertPageBreak
Inserts a page break at the insertion point
109
Alt + Shift + P
InsertPageField
Inserts a page number field
110
Ctrl + Shift + F3
InsertSpike
Empties the spike AutoText entry and inserts all of its contents into the document
111
Alt + Shift + T
InsertTimeField
Inserts a time field
112
Ctrl + I
Italic
Makes the selection italic (toggle)
113
Ctrl + J
JustifyPara
Aligns the paragraph at both the left and the right indent
114
Ctrl + L
LeftPara
Aligns the paragraph at the left indent
115
Down arrow
LineDown
Moves the insertion point down one line
116
Shift + down arrow
LineDownExtend
Extends the selection down one line
117
Up arrow
LineUp
Moves the insertion point up one line
118
Shift + up arrow
LineUpExtend
Extends the selection up one line
119
Ctrl + F11
LockFields
Locks the selected fields to prevent updating
120
Alt + Shift + K
MailMergeCheck
Checks for errors in a mail merge
121
Alt+Shift+E
MailMergeEditDataSource
Lets you edit a mail merge data source
122
Alt + Shift + N
MailMergeToDoc
Collects the results of the mail merge in a document
123
Alt Shift + M
MailMergeToPrinter
Sends the results of the mail merge to the printer
124
Alt + Shift + I
MarkCitation
Marks the text you want to include in the table of authorities
125
Alt + Shift + X
MarkIndexEntry
Marks the text you want to include in the index
126
Alt + Shift + O
MarkTableOfContentsEntry
Inserts a TC field (but it is far better to use Heading Styles to generate your Table of Contents instead)
127
Alt or F10
MenuMode
Makes the menu bar active
128
Alt + Shift + F11
MicrosoftScriptEditor
Starts or switches to Microsoft Development Environment application, allowing you to view the HTML/XML source code that would be behind the document if it were in ..htm format (or that is behind it if it already is in .htm format).
129
Alt + Ctrl + F1
MicrosoftSystemInfo
Execute the Microsoft System Info application
130
F2
MoveText
Moves the selection to a specified location without using the clipboard (press Return to execute the more)
131
Tab
NextCell
Moves to the next table cell
132
F11
NextField
Moves to the next field
133
Alt + F7
NextMisspelling
Find next spelling error
134
Alt + down arrow
NextObject
Moves to the next object on the page
135
Ctrl + F6
NextWindow
Switches to the next document window, equivalent to selecting a document from the Window menu.
136
Ctrl+Shift+N
NormalStyle
Applies the Normal style
137
Ctrl + 0
OpenOrCloseUpPara
Sets or removes extra spacing above the selected paragraph
138
F6
OtherPane
Switches to another window pane in Normal View (for instance, if you have if you have a Footnotes pane open in Normal view and want to switch to the main document and back without closing the pane).
139
Alt + _
OutlineCollapse
Collapses an Outline in Outline View by one level
140
Alt+Shift+rt arrow
OutlineDemote
Demotes the selected paragraphs one heading level
141
Alt + +
OutlineExpand
Expands an Outline in Outline View by one level
142
Alt+Shift+down arrow
OutlineMoveDown
Moves the selection below the next item in the outline
143
Alt+Shift+up arrow
OutlineMoveUp
Moves the selection above the previous item in the outline
144
Alt+Shift+left arrow
OutlinePromote
Promotes the selected paragraphs one heading level
145
Alt + Shift + L
OutlineShowFirstLine
Toggles between showing the first line of each paragraph only or showing all of the body text in the outline
146
Ins
Overtype
Toggles the typing mode between replacing and inserting
147
PgDn
PageDown
Moves the insertion point and document display to the next screen of text
148
Shift+ PgDn
PageDownExtend
Extends the selection and changes the document display to the next screen of text
149
PgUp
PageUp
Moves the insertion point and document display to the previous screen of text
150
Shift + PgUp
PageUpExtend
Extends the selection and changes the document display to the previous screen of text
151
Ctrl + down arrow
ParaDown
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the next paragraph
152
Shift + Ctrl + down arrow
ParaDownExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the next paragraph
153
Ctrl + up arrow
ParaUp
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the previous paragraph
154
Shift + Ctrl + up arrow
ParaUpExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the previous paragraph
155
Ctrl+Shift+V
PasteFormat
Applies the previously copied formatting to selection
156
Shift + Tab
PrevCell
Moves to the previous table cell
157
Shift + F11
PrevField
Moves to the previous field
158
Alt + up arrow
PrevObject
Moves to the previous object on the page
159
Ctrl + Shift + F6
PrevWindow
Switches back to the previous document window
160
Sfift+F4
RepeatFind
Repeats Go To or Find to find the next occurrence
161
Ctrl+Spacebar
ResetChar
Makes the selection the default character format of the applied style
162
Ctrl+Q
ResetPara
Makes the selection the default paragraph format of the applied style
163
Ctrl +R
RightPara
Aligns the paragraph at the right indent
164
Ctrl + *
ShowAll
Shows/hides all nonprinting characters
165
Alt + Shift + A
ShowAllHeadings
Displays all of the heading levels and the body text in Outline View
166
Ctrl + <
ShrinkFont
Decreases the font size of the selection
167
Ctrl + [
ShrinkFontOnePoint
Decreases the font size of the selection by one point
168
Ctrl + Shift + K
SmallCaps
Makes the selection small capitals (toggle)
169
Ctrl + 1
SpacePara1
Sets the line spacing to single space
170
Ctrl + 5
SpacePara15
Sets the line spacing to one-and-one-half space
171
Ctrl + 2
SpacePara2
Sets the line spacing to double space
172
Ctrl + F3
Spike
Deletes the selection and adds it to the "Spike" AutoText entry (which allows you to move text and graphics from nonadjacent locations)
173
Alt + PgUp
StartOfColumn
Moves to the first cell in the current column
174
Ctrl+Shift+Home
StartOfDocExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the first line of the document
175
Ctrl +Home
StartOfDocument
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the first line of the document
176
Home
StartOfLine
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the current line
177
Shift+Home
StartOfLineExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the current line
178
Alt+Home
StartOfRow
Moves to the first cell in the current row
179
Alt+Ctrl+PgUp
StartOfWindow
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the first visible line on the screen
180
Shift+ Alt+Ctrl+PgUp
StartOfWindowExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the first visible line on the screen
181
Strl + Shift + S
Style
Activates the Style drop-down on the Formatting toolbar
182
Ctrl + =
Subscript
Makes the selection subscript (toggle)
183
Ctrl + +
Superscript
Makes the selection superscript (toggle)
184
Ctrl + Shift + Q
SymbolFont
Applies the Symbol font to the selection
185
Alt A, F
TableAutoFormat
Applies a set of formatting to a table
186
Alt A, H
TableHeadings
Toggles table headings attribute on and off
187
Alt + click
(Alt + drag to select several)
TableSelectColumn
Selects the current column in a table
188
Click in left margin
TableSelectRow
Selects the current row in a table
189
Alt + double-click
TableSelectTable
Selects an entire table
190
Alt + Ctrl + U
TableUpdateAutoFormat
Updates the table formatting to match the applied Table Autoformat settings
191
Shift + F9 (Alt + F9 toggles all field codes on or off)
ToggleFieldDisplay
Shows the field codes or the results for the selection (toggle)
192
Alt T, C
ToolsCustomize
Allows you to customizes the Word user interface (menus, keyboard and toolbars) and store the customizations in a template (defaults to Normal.dot, so be careful!)
193
Alt + F8
ToolsMacro
Runs, creates, deletes, or revises a macro
194
F7
ToolsProofing
Checks the spelling and grammar in the active document
195
Ctr.l + Shift + E
ToolsRevisionMarksToggle
Toggles track changes for the active document
196
Shift + F7
ToolsThesaurus
Finds a synonym for the selected word
197
Ctrl+U
Underline
Formats the selection with a continuous underline (toggle)
198
Ctrl + Shift + T
(or drag the ruler)
UnHang
Decreases the hanging indent
199
Ctrl + Shift + M
(or drag the ruler)
UnIndent
Moves the left indent to the previous tab stop
200
Ctrl+Shift+F9
UnlinkFields
Permanently replaces the field codes with the results
201
Ctrl + Shift + F11
UnlockFields
Unlocks the selected fields for updating
202
F9
UpdateFields
Updates and displays the results of the selected fields
203
Ctrl + Shiift + F7
UpdateSource
Copies the modified text of a linked file back to its source file
204
Hover over comment
ViewAnnotations
Show or hide the comment pane
205
Dbl-click the endnote reference
ViewEndnoteArea
If in Normal View, opens a pane for viewing and editing the endnote (toggle). If in Page/Print Layout View, switches from the body text to the endnote or vice versa
206
At + F9
ViewFieldCodes
Shows the field codes or results for all fields (toggle)
207
Dbl-click the footnote reference
ViewFootnoteArea
If in Normal View, opens a pane for viewing and editing the footnote (toggle). If in Page/Print Layout View, switches from the body text to the footnote or vice versa.
208
Alt V, F
ViewFootnotes
If in Normal View, opens a pane for viewing and editing footnotes and endnotes (toggle). If in Page/Print Layout View, switches from the body text to the footnotes/endnotes or vice versa.
209
Alt V, H
ViewHeader
Displays header in page layout view
210
Alt V, N
(or Alt + Ctrl + N)
ViewNormal
Changes the editing view to normal view
211
Alt V, O
(or Alt + Ctrl + O)
ViewOutline
Displays a document's outline
212
Alt V, P
(or Alt + Ctrl + P)
ViewPage
Displays the page more-or-less as it will be printed, and allows editing (In Word 2000 the menu item is called Print Layout, but fortunately the command hasn't changed.
213
Alt + F11
ViewVBCode
Shows the VB editing environment (Tools + Macro + Visual Basic Editor)
214
Alt + left arrow
WebGoBack
Backward hyperlink (useful if you clicked on a page number hyperlink in the table of contents and then want to return to the TOC)
215
Alt + rt arrow
WebGoForward
Forward hyperlink
216
Alt W, A
WindowArrangeAll
Arranges windows as non-overlapping tiles
217
Ctrl + left arrow
WordLeft
Moves the insertion point to the left one word
218
Shift + Ctrl + left arrow
WordLeftExtend
Extends the selection to the left one word
219
Ctrl + rt arrow
WordRight
Moves the insertion point to the right one word
220
Shift + Ctrl + rt arrow
WordRightExtend
Extends the selection to the right one word
221
Ctrl + Shift + W
WordUnderline
Underlines the words but not the spaces in the selection (toggle)
Disclaimer:
This Blog Contain all the Content only for information, all link provide for educational purpose, so any one find the content of these blog similar with us, its a co instant only, this blog not for legal authentication, content should be use by various origin/other website, so DO NOT clime for copyright activities.
Ctrl + Shift + A
AllCaps
Makes the selection all capitals (toggle)
2
Alt + Ctrl + 1
ApplyHeading1
Applies Heading 1 style to the selected text
3
Alt + Ctrl + 2
ApplyHeading2
Applies Heading 2 style to the selected text
4
Alt + Ctrl + 3
ApplyHeading3
Applies Heading 3 style to the selected text
5
Ctrl + Shift + L
ApplyListBullet
Applies List Bullet style to the selected text
6
Alt + F10
AppMaximize
Enlarges the application window to full size
7
Alt + F5
AppRestore
Restores the application window to normal size
8
Ctrl+B
Bold
Makes the selection bold (toggle)
9
Ctrl + PgDn
BrowseNext
Jump to the next browse object
10
Ctrl + PgUp
BrowsePrev
Jump to the previous browse object
11
Alt + Ctrl + Home
BrowseSel
Select the next/prev browse object
12
Esc
Cancel
Terminates an action
13
Ctrl+E
CenterPara
Centers the paragraph between the indents
14
Shift+F3
ChangeCase
Changes the case of the letters in the selection
15
Left arrow
CharLeft
Moves the insertion point to the left one character
16
Shift + Left arrow
CharLeftExtend
Extends the selection to the left one character
17
Rt arrow
CharRight
Moves the insertion point to the right one character
18
Shift + Rt arrow
CharRightExtend
Extends the selection to the right one character
19
Alt + Shift + C
ClosePane
Closes the active window pane (if you are in Normal View and have, for example, the Footnote pane open)
20
Alt+Drag (or press Ctrl + Shift + F8 and drag, but Alt + Drag is far easier!)
ColumnSelect
Selects a columnar block of text
21
Ctrl +Shift+C
CopyFormat
Copies the formatting of the selection
22
Shift + F2
CopyText
Makes a copy of the selection without using the clipboard (press Return to paste)
23
Alt + F3
CreateAutoText
Adds an AutoText entry to the active template
24
Ctrl+ Backspace
DeleteBackWord
Deletes the previous word without putting it on the Clipboard
25
Ctrl + Del
DeleteWord
Deletes the next word without putting it on the Clipboard
26
Ctrl+W, Ctrl+F4
DocClose
Prompts to save the document and then closes the active window. (But doesn't intercept the menu command)
27
Ctrl + F10
DocMaximize
Enlarges the active window to full size
28
Ctrl + F7
DocMove
Changes the position of the active window
29
Ctrl + F5
DocRestore
Restores the window to normal size
30
Ctrl + F8
DocSize
Changes the size of the active window
31
Alt + Ctrl + S
DocSplit
Splits the active window horizontally and then adjusts the split
32
Alt + Shift + F9
DoFieldClick
Executes the action associated with macrobutton fields
33
Ctrl + Shift + D
DoubleUnderline
Double underlines the selection (toggle)
34
Alt R, G
DrawGroup
Groups the selected drawing objects
35
Alt R, I
DrawSnapToGrid
Sets up a grid for aligning drawing objects
36
Alt R, U
DrawUngroup
Ungroups the selected group of drawing objects
37
Ctrl+Shift+F5 (Or: Alt I, K)
EditBookmark
Brings up the bookmark dialog
38
Del
EditClear
Performs a forward delete or removes the selection without putting it on the Clipboard
39
Ctrl+C
EditCopy
Copies the selection and puts it on the Clipboard
40
Ctrl+X
EditCut
Cuts the selection and puts it on the Clipboard
41
Ctrl+F
EditFind
Finds the specified text or the specified formatting
42
F5, Ctrl+G
EditGoTo
Jumps to a specified place in the active document
43
Alt E, K
EditLinks
Allows links to be viewed, updated, opened, or removed
44
Ctrl+V
EditPaste
Inserts the Clipboard contents at the insertion point
45
Alt E, S
EditPasteSpecial
Inserts the Clipboard contents as a linked object, embedded object, or other format
46
Alt + Shift + Backspc
EditRedo
Redoes the last action that was undone
47
F4
EditRedoOrRepeat
Repeats the last command, or redoes the last action that was undone (unfortunately, doesn't work for as many commands in Word 2000 as in Word 97 and below, but this is still one of Word's most useful shortcuts, if not the most useful)
48
Ctrl+H
EditReplace
Finds the specified text or the specified formatting and replaces it
49
Ctrl+A
EditSelectAll
Selects the entire document
50
Ctrl+Z
EditUndo
Reverses the last action
51
Alt + PageDn (to select to end of column, use Alt + Shift + PgDn)
EndOfColumn
Moves to the last cell in the current table column
52
Ctrl+Shift+End
EndOfDocExtend
Extends the selection to the end of the last line of the document
53
Ctrl+End
EndOfDocument
Moves the insertion point to the end of the last line of the document
54
End
EndOfLine
Moves the insertion point to the end of the current line
55
Shift+End
EndOfLineExtend
Extends the selection to the end of the current line
56
Alt+End
EndOfRow
Moves to the last cell in the current row
57
Alt + Ctrl + PgDn
EndOfWindow
Moves the insertion point to the end of the last visible line on the screen
58
Shift + Alt + Ctrl + PgDn
EndOfWindowExtend
Extends the selection to the end of the last visible line on the screen
59
F8 (press Esc to turn off)
ExtendSelection
Turns on extend selection mode and then expands the selection with the direction keys
60
Alt + F4 (<9>)
FileCloseOrExit
Closes the current document, or if no documents are open, quits Word. Horrible command, as it makes it a long winded business to quit Word. But there's a simple solution - assign Alt+F4 to FileExit instead.
61
Alt + F4 (Word 97)
FileExit
Quits Microsoft Word and prompts to save the documents (does intercept the menu item, but not the keyboard shortcut, or the x button. An AutoExit macro is usually a better way of intercepting this).
62
NOT Ctrl+N!!
FileNew
Creates a new document or template (brings up the dialog). Note that: Word pretends that Ctrl+N is assigned to FileNew but it isn't, it's assigned to FileNewDefault You can fix this in Word 2000 by assigning Ctrl+N to the FileNewDialog command. In Word 97 the only way to fix it is to create a macro called FileNew (to do this, press Alt + F8, type "FileNew" without the quotes and Click "Create". The macro will automatically contain the code needed to make it work).
63
Ctrl+N
FileNewDefault
Creates a new document based on the Normal template.
64
Ctrl+O
FileOpen
Opens an existing document or template
65
Alt F, U
FilePageSetup
Changes the page setup of the selected sections
66
Ctrl + P
FilePrint
Prints the active document (brings up the dialog)
67
Ctrl+F2
FilePrintPreview
Displays full pages as they will be printed
68
Alt F, I
FileProperties
Shows the properties of the active document
69
Ctrl+S
FileSave
FileSave
70
Alt F, A (or F12)
FileSaveAs
Saves a copy of the document in a separate file (brings up the dialog)
71
Ctrl+Shift+F
Font
Activates the Fonts listbox on the formatting toolbar
72
Ctrl+Shift+P
FontSizeSelect
Activates the Font Size drop-down on the formatting toolbar
73
Alt + Ctrl + K
FormatAutoFormat
Automatically formats a document (or sometimes, automatically screws it up)
74
Alt O, B
FormatBordersAndShading
Changes the borders and shading of the selected paragraphs, table cells, and pictures
75
Alt O, E
FormatChangeCase
Changes the case of the letters in the selection
76
Alt O, C
FormatColumns
Changes the column format of the selected sections (brings up the dialog)
77
Alt O, D
FormatDropCap
Formats the first character of current paragraph as a dropped capital (must select it first)
78
Ctrl+D
FormatFont
Brings up the Format + Font dialog
79
Alt + Shift + R
FormatHeaderFooterLink
Links the current header/footer to the previous section (but does not intercept the button on the Header Footer toolbar)
80
Alt O, P
FormatParagraph
Brings up the Format Paragraph dialog
81
Alt O, S
FormatStyle
Applies, creates, or modifies styles
82
Alt O, T
FormatTabs
Brings up the Format Tabs dialog
83
Shift + F5
GoBack
Returns to the previous insertion point (goes back to up to 3 points, then returns to where you started; this is one of the most useful shortcuts of them all. Also useful when opening a document, if you want to g straight to where you were last editing it)
84
Ctrl + >
GrowFont
Increases the font size of the selection
85
Ctrl + ]
GrowFontOnePoint
Increases the font size of the selection by one point
86
Ctrl + T (or drag the ruler)
HangingIndent
Increases the hanging indent
87
F1
Help
Microsoft Word Help
88
Shift + F1
HelpTool
Lets you get help on a command or screen region or examine text properties
89
Ctrl + Shift + H
Hidden
Makes the selection hidden text (toggle)
90
Click on it
HyperlinkOpen
Connect to a hyperlink's address
91
Ctrl + M (or drag the ruler)
Indent
Moves the left indent to the next tab stop
92
Alt + Ctrl + M (or Alt I, M)
InsertAnnotation
Inserts a comment
93
F3
InsertAutoText
Replaces the name of the AutoText entry with its contents
94
Alt I, B
InsertBreak
Ends a page, column, or section at the insertion point
95
Alt I, C
InsertCaption
Inserts a caption above or below a selected object
96
Ctrl + Shift + Return
InsertColumnBreak
Inserts a column break at the insertion point
97
Alt + Shift + D
InsertDateField
Inserts a date field
98
Alt + Ctrl + D
InsertEndnoteNow
Inserts an endnote reference at the insertion point without displaying the dialog
99
Alt I, F
InsertField
Inserts a field in the active document
100
Ctrl+F9
InsertFieldChars
Inserts an empty field with the enclosing field characters
101
Alt I, L
InsertFile
Inserts the text of another file into the active document
102
Alt I, N
InsertFootnote
Inserts a footnote or endnote reference at the insertion point
103
Alt + Ctrl + F
InsertFootnoteNow
Inserts a footnote reference at the insertion point without displaying the dialog
104
Ctrl + K
InsertHyperlink
Insert Hyperlink
105
Alt I, D
InsertIndexAndTables
Inserts an index or a table of contents, figures, or authorities into the document
106
Alt + Ctrl + L
InsertListNumField
Inserts a ListNum Field
107
Alt + Shift + F
InsertMergeField
Brings up a dialog to insert a mail merge field at the insertion point. (It does not intercept the button on the Mail merge. toolbar)
108
Ctrl + Return
InsertPageBreak
Inserts a page break at the insertion point
109
Alt + Shift + P
InsertPageField
Inserts a page number field
110
Ctrl + Shift + F3
InsertSpike
Empties the spike AutoText entry and inserts all of its contents into the document
111
Alt + Shift + T
InsertTimeField
Inserts a time field
112
Ctrl + I
Italic
Makes the selection italic (toggle)
113
Ctrl + J
JustifyPara
Aligns the paragraph at both the left and the right indent
114
Ctrl + L
LeftPara
Aligns the paragraph at the left indent
115
Down arrow
LineDown
Moves the insertion point down one line
116
Shift + down arrow
LineDownExtend
Extends the selection down one line
117
Up arrow
LineUp
Moves the insertion point up one line
118
Shift + up arrow
LineUpExtend
Extends the selection up one line
119
Ctrl + F11
LockFields
Locks the selected fields to prevent updating
120
Alt + Shift + K
MailMergeCheck
Checks for errors in a mail merge
121
Alt+Shift+E
MailMergeEditDataSource
Lets you edit a mail merge data source
122
Alt + Shift + N
MailMergeToDoc
Collects the results of the mail merge in a document
123
Alt Shift + M
MailMergeToPrinter
Sends the results of the mail merge to the printer
124
Alt + Shift + I
MarkCitation
Marks the text you want to include in the table of authorities
125
Alt + Shift + X
MarkIndexEntry
Marks the text you want to include in the index
126
Alt + Shift + O
MarkTableOfContentsEntry
Inserts a TC field (but it is far better to use Heading Styles to generate your Table of Contents instead)
127
Alt or F10
MenuMode
Makes the menu bar active
128
Alt + Shift + F11
MicrosoftScriptEditor
Starts or switches to Microsoft Development Environment application, allowing you to view the HTML/XML source code that would be behind the document if it were in ..htm format (or that is behind it if it already is in .htm format).
129
Alt + Ctrl + F1
MicrosoftSystemInfo
Execute the Microsoft System Info application
130
F2
MoveText
Moves the selection to a specified location without using the clipboard (press Return to execute the more)
131
Tab
NextCell
Moves to the next table cell
132
F11
NextField
Moves to the next field
133
Alt + F7
NextMisspelling
Find next spelling error
134
Alt + down arrow
NextObject
Moves to the next object on the page
135
Ctrl + F6
NextWindow
Switches to the next document window, equivalent to selecting a document from the Window menu.
136
Ctrl+Shift+N
NormalStyle
Applies the Normal style
137
Ctrl + 0
OpenOrCloseUpPara
Sets or removes extra spacing above the selected paragraph
138
F6
OtherPane
Switches to another window pane in Normal View (for instance, if you have if you have a Footnotes pane open in Normal view and want to switch to the main document and back without closing the pane).
139
Alt + _
OutlineCollapse
Collapses an Outline in Outline View by one level
140
Alt+Shift+rt arrow
OutlineDemote
Demotes the selected paragraphs one heading level
141
Alt + +
OutlineExpand
Expands an Outline in Outline View by one level
142
Alt+Shift+down arrow
OutlineMoveDown
Moves the selection below the next item in the outline
143
Alt+Shift+up arrow
OutlineMoveUp
Moves the selection above the previous item in the outline
144
Alt+Shift+left arrow
OutlinePromote
Promotes the selected paragraphs one heading level
145
Alt + Shift + L
OutlineShowFirstLine
Toggles between showing the first line of each paragraph only or showing all of the body text in the outline
146
Ins
Overtype
Toggles the typing mode between replacing and inserting
147
PgDn
PageDown
Moves the insertion point and document display to the next screen of text
148
Shift+ PgDn
PageDownExtend
Extends the selection and changes the document display to the next screen of text
149
PgUp
PageUp
Moves the insertion point and document display to the previous screen of text
150
Shift + PgUp
PageUpExtend
Extends the selection and changes the document display to the previous screen of text
151
Ctrl + down arrow
ParaDown
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the next paragraph
152
Shift + Ctrl + down arrow
ParaDownExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the next paragraph
153
Ctrl + up arrow
ParaUp
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the previous paragraph
154
Shift + Ctrl + up arrow
ParaUpExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the previous paragraph
155
Ctrl+Shift+V
PasteFormat
Applies the previously copied formatting to selection
156
Shift + Tab
PrevCell
Moves to the previous table cell
157
Shift + F11
PrevField
Moves to the previous field
158
Alt + up arrow
PrevObject
Moves to the previous object on the page
159
Ctrl + Shift + F6
PrevWindow
Switches back to the previous document window
160
Sfift+F4
RepeatFind
Repeats Go To or Find to find the next occurrence
161
Ctrl+Spacebar
ResetChar
Makes the selection the default character format of the applied style
162
Ctrl+Q
ResetPara
Makes the selection the default paragraph format of the applied style
163
Ctrl +R
RightPara
Aligns the paragraph at the right indent
164
Ctrl + *
ShowAll
Shows/hides all nonprinting characters
165
Alt + Shift + A
ShowAllHeadings
Displays all of the heading levels and the body text in Outline View
166
Ctrl + <
ShrinkFont
Decreases the font size of the selection
167
Ctrl + [
ShrinkFontOnePoint
Decreases the font size of the selection by one point
168
Ctrl + Shift + K
SmallCaps
Makes the selection small capitals (toggle)
169
Ctrl + 1
SpacePara1
Sets the line spacing to single space
170
Ctrl + 5
SpacePara15
Sets the line spacing to one-and-one-half space
171
Ctrl + 2
SpacePara2
Sets the line spacing to double space
172
Ctrl + F3
Spike
Deletes the selection and adds it to the "Spike" AutoText entry (which allows you to move text and graphics from nonadjacent locations)
173
Alt + PgUp
StartOfColumn
Moves to the first cell in the current column
174
Ctrl+Shift+Home
StartOfDocExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the first line of the document
175
Ctrl +Home
StartOfDocument
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the first line of the document
176
Home
StartOfLine
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the current line
177
Shift+Home
StartOfLineExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the current line
178
Alt+Home
StartOfRow
Moves to the first cell in the current row
179
Alt+Ctrl+PgUp
StartOfWindow
Moves the insertion point to the beginning of the first visible line on the screen
180
Shift+ Alt+Ctrl+PgUp
StartOfWindowExtend
Extends the selection to the beginning of the first visible line on the screen
181
Strl + Shift + S
Style
Activates the Style drop-down on the Formatting toolbar
182
Ctrl + =
Subscript
Makes the selection subscript (toggle)
183
Ctrl + +
Superscript
Makes the selection superscript (toggle)
184
Ctrl + Shift + Q
SymbolFont
Applies the Symbol font to the selection
185
Alt A, F
TableAutoFormat
Applies a set of formatting to a table
186
Alt A, H
TableHeadings
Toggles table headings attribute on and off
187
Alt + click
(Alt + drag to select several)
TableSelectColumn
Selects the current column in a table
188
Click in left margin
TableSelectRow
Selects the current row in a table
189
Alt + double-click
TableSelectTable
Selects an entire table
190
Alt + Ctrl + U
TableUpdateAutoFormat
Updates the table formatting to match the applied Table Autoformat settings
191
Shift + F9 (Alt + F9 toggles all field codes on or off)
ToggleFieldDisplay
Shows the field codes or the results for the selection (toggle)
192
Alt T, C
ToolsCustomize
Allows you to customizes the Word user interface (menus, keyboard and toolbars) and store the customizations in a template (defaults to Normal.dot, so be careful!)
193
Alt + F8
ToolsMacro
Runs, creates, deletes, or revises a macro
194
F7
ToolsProofing
Checks the spelling and grammar in the active document
195
Ctr.l + Shift + E
ToolsRevisionMarksToggle
Toggles track changes for the active document
196
Shift + F7
ToolsThesaurus
Finds a synonym for the selected word
197
Ctrl+U
Underline
Formats the selection with a continuous underline (toggle)
198
Ctrl + Shift + T
(or drag the ruler)
UnHang
Decreases the hanging indent
199
Ctrl + Shift + M
(or drag the ruler)
UnIndent
Moves the left indent to the previous tab stop
200
Ctrl+Shift+F9
UnlinkFields
Permanently replaces the field codes with the results
201
Ctrl + Shift + F11
UnlockFields
Unlocks the selected fields for updating
202
F9
UpdateFields
Updates and displays the results of the selected fields
203
Ctrl + Shiift + F7
UpdateSource
Copies the modified text of a linked file back to its source file
204
Hover over comment
ViewAnnotations
Show or hide the comment pane
205
Dbl-click the endnote reference
ViewEndnoteArea
If in Normal View, opens a pane for viewing and editing the endnote (toggle). If in Page/Print Layout View, switches from the body text to the endnote or vice versa
206
At + F9
ViewFieldCodes
Shows the field codes or results for all fields (toggle)
207
Dbl-click the footnote reference
ViewFootnoteArea
If in Normal View, opens a pane for viewing and editing the footnote (toggle). If in Page/Print Layout View, switches from the body text to the footnote or vice versa.
208
Alt V, F
ViewFootnotes
If in Normal View, opens a pane for viewing and editing footnotes and endnotes (toggle). If in Page/Print Layout View, switches from the body text to the footnotes/endnotes or vice versa.
209
Alt V, H
ViewHeader
Displays header in page layout view
210
Alt V, N
(or Alt + Ctrl + N)
ViewNormal
Changes the editing view to normal view
211
Alt V, O
(or Alt + Ctrl + O)
ViewOutline
Displays a document's outline
212
Alt V, P
(or Alt + Ctrl + P)
ViewPage
Displays the page more-or-less as it will be printed, and allows editing (In Word 2000 the menu item is called Print Layout, but fortunately the command hasn't changed.
213
Alt + F11
ViewVBCode
Shows the VB editing environment (Tools + Macro + Visual Basic Editor)
214
Alt + left arrow
WebGoBack
Backward hyperlink (useful if you clicked on a page number hyperlink in the table of contents and then want to return to the TOC)
215
Alt + rt arrow
WebGoForward
Forward hyperlink
216
Alt W, A
WindowArrangeAll
Arranges windows as non-overlapping tiles
217
Ctrl + left arrow
WordLeft
Moves the insertion point to the left one word
218
Shift + Ctrl + left arrow
WordLeftExtend
Extends the selection to the left one word
219
Ctrl + rt arrow
WordRight
Moves the insertion point to the right one word
220
Shift + Ctrl + rt arrow
WordRightExtend
Extends the selection to the right one word
221
Ctrl + Shift + W
WordUnderline
Underlines the words but not the spaces in the selection (toggle)
Disclaimer:
This Blog Contain all the Content only for information, all link provide for educational purpose, so any one find the content of these blog similar with us, its a co instant only, this blog not for legal authentication, content should be use by various origin/other website, so DO NOT clime for copyright activities.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)